Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the graphical representation of the electromotive force (emf) induced in a coil by a bar magnet spinning perpendicular to the coil's axis. Participants explore the nature of the waveform produced, including its characteristics and the underlying principles of electromagnetic induction.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
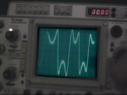
- Some participants propose that the induced emf would resemble a sinewave, while others suggest it may be an irregular sinewave due to the alternating N and S poles of the spinning magnet.
- One participant questions whether the amplitude of the induced emf would be zero if the bar magnet's axis is perpendicular to the coil's axis, arguing that the total flux through the coil area remains constant.
- Another participant emphasizes that the voltage is generated by the changing flux through the area surrounded by the coil, rather than simply by the poles of the magnet passing by.
- Some participants discuss the complexity of accurately representing the magnetic flux from a bar magnet and the implications for the waveform produced.
- There is a suggestion that if the magnetic field near the bar magnet is approximated as homogeneous, the resulting voltage could be a sinewave, but the accuracy of this assumption is questioned.
- One participant expresses skepticism about the existence of a simple expression for the magnetic flux from a bar magnet and the feasibility of generating proper sinewaves in practical applications.
- Several participants debate the characteristics of the waveform, including the presence of double positive and negative peaks, and the conditions under which these features might arise.
- There is a discussion about the relationship between the distance of the magnet from the coil and the effect on the induced voltage, with some arguing that the voltage peaks occur at points of maximum flux change.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express multiple competing views regarding the nature of the induced emf waveform, with no consensus reached on the exact characteristics or the underlying mechanisms. The discussion remains unresolved with differing interpretations of the effects of the magnet's rotation and its geometry.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight limitations in their assumptions regarding the geometry of the system, the nature of the magnetic field, and the complexities involved in accurately modeling the induced emf. The discussion reflects a range of perspectives on how these factors influence the resulting waveform.