You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Magnetic: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Magnetism is a class of physical attributes that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomenon of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ferro- refers to iron, because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4.
All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminum and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an applied magnetic field; diamagnetic substances, such as copper and carbon, are weakly repelled; while antiferromagnetic materials, such as chromium and spin glasses, have a more complex relationship with a magnetic field. The force of a magnet on paramagnetic, diamagnetic, and antiferromagnetic materials is usually too weak to be felt and can be detected only by laboratory instruments, so in everyday life, these substances are often described as non-magnetic.
The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature, pressure, and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.
The strength of a magnetic field almost always decreases with distance, though the exact mathematical relationship between strength and distance varies. Different configurations of magnetic moments and electric currents can result in complicated magnetic fields.
Only magnetic dipoles have been observed, although some theories predict the existence of magnetic monopoles.
View More On Wikipedia.org
All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminum and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an applied magnetic field; diamagnetic substances, such as copper and carbon, are weakly repelled; while antiferromagnetic materials, such as chromium and spin glasses, have a more complex relationship with a magnetic field. The force of a magnet on paramagnetic, diamagnetic, and antiferromagnetic materials is usually too weak to be felt and can be detected only by laboratory instruments, so in everyday life, these substances are often described as non-magnetic.
The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature, pressure, and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.
The strength of a magnetic field almost always decreases with distance, though the exact mathematical relationship between strength and distance varies. Different configurations of magnetic moments and electric currents can result in complicated magnetic fields.
Only magnetic dipoles have been observed, although some theories predict the existence of magnetic monopoles.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
M
I What is the effect of a magnetic field on an atom's magnetic moment?
Hello! I want to make sure I understand (mainly qualitatively) what happens to an atom in a magnetic field. Assume we have an atom with an even number of protons and electrons. This means that all proton (electrons) are paired up, except for one of them (I am not totally sure if this pairing is...- Malamala
- Thread
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Magnetic field of a point charge moving uniformly
Everywhere I look online I see the formula for the magnetic field of a uniformly moving charge is, $$\frac{\mu_0 q \vec v \times \vec r}{4\pi r^3}$$ but when I calculate it by transforming the electrostatic field (taking the motion along x) I get, $$\frac{\gamma \mu_0 q \vec v \times \vec...- Hiero
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
Magnetic mirror concept -- electrons vs ions
I am reading a book on fusion and just went over a paragraph of magnetic mirror confinement. What I want to understand is this. So all charged particles gyrate around magnetic field lines and if they have also a velocity parallel to the field they form helical paths. The gyroradius is... -
D
How to calculate magnetic braking force?
I want to know how to calculate the braking force acting on a magnet falling through a copper tube. The setup can be seen in this video (YouTube, @ 1:49 - 3:12): Copper's Surprising Reaction to Strong Magnets. Note that it's not a copper tube in the video but a plastic tube surrounded by a...- dishwasher95
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
P
What is the mistake in calculating the magnetic field in this problem?
The problem is simple, but have one confusion, if i substitute the values given, I get ## B = \frac {10^{-7}(6*10^{-6})[(8*10^6 \vec j) \times (-0.5\vec j + 0.5 \vec k)]} {r^2} ## ## B = 48\mu T\vec i## First thing the answer does not match. I don't see the angle in calculations between ##\vec...- Physicslearner500039
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Field Magnetic Magnetic field
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Non magnetic linear displacement system for moving a Hall Sensor
Dear mechanical expert I have to realize a linear displacement system for a Hall sensor that has to slide along the central axis of a narrow cylinder and with which high intensity magnetic field measurements (1-14 Tesla) have to be made. The field is produced by a commercial vertical magnet...- maxim
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
P
Finding the Magnetic force on the coil
Surely a tough one, I am doing it from the basics. This is the diagram i tried to draw showing the Force and current I The Length L is the tangent to the circle. The Force F is pointing upwards at ##90 Deg## to the ##\vec B## and also perpendicular to ##\vec L##. I am considering a small...- Physicslearner500039
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Coil Force Magnetic Magnetic force
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Calculation of Change in Magnetic Flux Linkage of a moving wire
Can anyone explain the above answer to me? What does the "change in area" mean?- Jy158654
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How do magnetic fields behave in superposition?
Homework Statement:: n/a Relevant Equations:: n/a These are the answers diagrams, with my questions in red. 1. In arrangement 1, I was wondering why there isn't any magnetic lines inside the magnet. While it seems that vector addition would make the field go outside the magnetic-less...- aspodkfpo
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Magnetic Superposition
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Find the magnitude and direction of the Magnetic field required
i tried to draw the directions of the parameters The direction of B is clear since then the Force will be in the positive X direction. I am bit confused with the direction of Force, how would i draw it and the components. Is the gravitational force i have drawn is correct? Do we have better...- Physicslearner500039
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Difference in these two concepts of Magnetic Torque
I am confused with the concept of Torque handled differently in books, Concept1: If a loop is placed in a magnetic field and the current flowing in the loop is ##I## there will be force and torque acting on the loop given by ##F = I \vec l \times \vec B ##. The torque is given by ##\tau =\vec...- Physicslearner500039
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-

Verifying Coordinate System for Electric and Magnetic Forces
The attached file is the coordinate system I've used a) $$\vec{E}=\dfrac{\vec{F_e}}{q}=\dfrac{1,10\cdot{10^{-13}}\hat{j}\;N}{1,6\cdot{10^{-19}}\;C}=6,88\cdot{10^5}\hat{j}\;N/C$$ b) $$\sum{\vec{F_{net}}}=\vec{0}=\vec{F_e}+\vec{F_m}$$...- mcastillo356
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
I Electron's magnetic moment
Is Peskin and Schroeder book, page 187 when they try to connect the electron form factors to its magnetic moment they get the expression $$\bar{u}(p')\left(\gamma^i F_1(q^2)+\frac{i \sigma^{i\nu}q_\nu}{2m}F_2(q^2)\right)u(p)$$ Where ##p##, ##p'## are the momenta on on-shell electrons and...- Gaussian97
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

Magnetic Flux outside of a long solenoid
I have been reading Griffith's Introduction to Electodynamics and i am currently at the chapter about magnetostatics. There is an example about a long solenoid with n units per length and radius R that shows a way of finding the magnetic vector potential. The magnetic field inside the solenoid...- lelouch_v1
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Hypothetical discussion on the effect of magnetic fields on planets
Ok, so I have long been fascinated with magnetic fields and their mysterious nature. I've been wondering what would happen when the magnetic field of Earth gets bent/disturbed/rippled by some extraneous force. I am aware the extent of effects that magnetic fields have on a planet is great, but I...- Epsilon Eridani
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Earth Sciences
-

Calculating the magnetic field in this seemingly simple case?
A classic example in textbooks is calculating the magnetic field inside a solenoid of length ##l## with ##N## turns and making the assumption that the magnetic field inside the solenoid is pretty uniform and outside it is 0. Using Ampere's law ## \oint_C \vec B \cdot d \vec l = \mu_0 I_{through}...- Abdullah Almosalami
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Field Magnetic Magnetic field
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Angle of deviation from a magnetic field
The beam of protons are directed towards the axis of the cylinder, perpendicular to the direction of the field. While traveling through the cross-section of the cylinder, the proton beam experiences a magnetic force, which tends to move the beam in a circular orbit of the radius given by: r =...- tanaygupta2000
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Is diamagnetism only present with varying magnetic fields?
Hello. I was wondering if diamagnetic materials only repel varying electric field? By Ampere law only a variable flux can cause an electromotive force, so, and by what I understood diamagnetism is explained exclusively by Ampere law. Am I wrong?- jaumzaum
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
E
Force derived from magnetic energy of a current carrying spring
The magnetic energy of a current carrying spring, with ##N## turns, length ##x## and cross sectional area ##A##, is $$E_m = \frac{\mu_0 N^2 I^2 A}{2x}$$The (negated) spatial derivative of this yields a quantity with dimensions of force,$$F = - \frac{dE_m}{dx} = \frac{\mu_0 N^2 I^2 A}{2x^2}$$How...- etotheipi
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
E
Ball rolling in a magnetic field
I first found the Lorentz force on the ball as a whole$$\vec{F}_m = \iiint_V \rho(\omega \times \vec{r} + \vec{V})\times \vec{B} dV = \rho \vec{\omega} \times \left( \iint_V \vec{r} dV \right) \times \vec{B} + \rho \iiint_V \vec{V} \times \vec{B} dV = Q\vec{V} \times \vec{B}$$due to the...- etotheipi
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
What is the origin of magnetic potential energy?
Recently I have encountered the following expression for the potential energy of a magnetic dipole of moment ##\boldsymbol{\mu}## placed in an external magnetostatic field B: $$U=-\boldsymbol{\mu} \cdot \textbf{B}$$. However, I was told that magnetic fields are non-conservative, so we can't...- KDPhysics
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
Magnetic mirror: pentagon or hexagon toroid?
I know that the problem of magnetic mirrors is that they leak out the tight ends of the mirror, on the other hand the main problem of toroids is that magnetic field line curvature creates a better confinement on the inner diameter and lesser on the outer diameter so needs a strong plasma current... -
L
Magnetic field of a rotating disk with a non-uniform volume charge
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This was a problem introduced during my classical electrodynamics course. I am not 100% sure, but I think I've solved up to problems (a) and (b) as...- Light bulB 6626
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
F
Why does an alpha particle curve less in a magnetic field than a beta?
Suppose you are analyzing this image. The question to answer is: Explain why the alpha particle's path has a larger radius than either of the beta particle paths. Justify your answer using either momentum or charge-to-mass ratio. When you are answering this, suppose you know that , in...- flintstones
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Cylindrical Halbach array with a vertical magnetic field?
Similar to what is shown here, except the south side would be the weak side of the array. A link to purchase one of these or at least the magnetic field arrangement would be very helpful. Thanks in advance.- rayjbryant
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Vector potential ##\vec A## in terms of magnetic field ##\vec B##
My solution is making an analogy of the ##\text{Relevant equations}## as shown above, starting from the equation ##\vec \omega = \frac{1}{2} \vec \nabla \times \vec v##. We have ##\vec B = \vec \nabla \times \vec A = \frac{1}{2} \vec \nabla \times 2\vec A \Rightarrow 2\vec A = \vec B \times...- brotherbobby
- Thread
- Replies: 26
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Deflection of magnetic dipoles by a magnetic field
I'm reading about the Stern–Gerlach experiment and the only part that confuses me is how a magnetic field would deflect particles with magnetic dipoles instead of just rotating them. In this case the magnetic field is non-uniform, but it still seems intuitively strange to me since magnetic...- snoopies622
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
H
Deflection of a Magnet in an Inhomogenous Magnetic Field
Say I've got a magnet flying through empty space in a homogenous magnetic field. The magnet precesses and flies in a straight path. Now make that magnetic field inhomogenous. The magnet precesses and flies in a curved path. What I can't figure out is why the path is curved. It is because...- Hornbein
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Force acting on a current carrying conductor within a magnetic field
I am new to this forum, and this is my first post. Please bear with me if my query has any inaccuracies. In the attached figure, a coil is wrapped around the central arm of a flat H-shaped thin metallic plate (such as iron). DC current flows through the coil and magnetizes the arm. At the...- sss
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Does moving an insulating cylinder produce a magnetic field?
Suppose that we have an insulating cylinder with ##\rho_q##. If i move the cylinder towards ##+\hat{n}##, will it produce a magnetic field? My assumption is that since we have an insulator, then the electrons are bound and there cannot be a current, thus a magnetic field is not produced. Also...- lelouch_v1
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

What does a magnetic field feel like?
https://blog.nationalgeographic.org/2014/01/03/dogs-sense-Earth's-magnetic-field/"...the first study showing a mammal not only being able to sense it, but also to exhibit a specific behavior in response to natural magnetic field variations. " In my view, dogs are nearer human consciousness than...- DaveC426913
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Field Magnetic Magnetic field
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Biology and Medical
-

Magnetic field for a capacitor
.- Fabio97
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
A Questions about magnetic monopoles
So far as I know there are no monopoles in the electro-weak sector of standard model. So people look for it in the GUT and SUSY sectors. However, they are predicted to be heavy(order of Planck mass). There have been studies from LHC attempting to detect monopoles. So here are my questions: 1...- phoenix95
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-

Properties of symmetric magnetic field around ##Z## axis (cylinder)
I am trying to understand but without a succes why symmetric magnetic field around ##Z## axis make that ##\hat \phi## magnetic field is zero I can't understand why it physically happens and also how can I derive it mathematically? What does the word symmetric means when talking about magnetic...- sagigever
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
F
Non-circular motion of a particle in a perpendicular constant magnetic field
There's a constant magnetic field B. If a particle is acted on by a force qv*B (* cross) only, and the initial velocity v0 is normal to B, is the motion certainly a circular one (for any m, q, v0)? mv''=qv*B If one solves this equation (vector), it doesn't seem obvious.- feynman1
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
G
Confusion on the magnitude of magnetic fields
Here, the correct options are A,D. Solution: I got A as answer as ∫ B.dl=µI. But, the answer to the question says that it is a solenoid and therefore Bx=0 for point P. Here I'm a bit confused. I know this system resembles a solenoid in some ways, then By must have some finite value, but...- Gourab_chill
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Magnetic field in a rotating uniformly-charged infinite cylinder
I am sure I need to use Amper's law to do that. if I use the equation I mentioned above it easy to calculate the right side of the equation but I have problem how to calculate the path integral. I know from right hand rule that the magnetic field will point at $$Z$$ and the current is in...- sagigever
- Thread
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Force & energy in cutting and stretching magnetic field lines?
I have an ordinary switchable magnet for holding tools to a lathe. It's like a magnetic force gearbox, but I can't quite understand the force multiplication. When placed on a steel surface the switch force is approximately ~5N on both finger and thumb at 1.5cm radius acting over a 3cm arc...- Luke2642
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
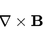
Magnetic field (correction term)
Ampere´'s law with the correction term I have a infinite cylinder with radius R with a current density , and magnetic field . I have to proof that it is acceptable to discard the correction term of term of ampere's law, while calculating the magnetic field, as long as it obeys the following...- anaisabel
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

EM: Separation of variables to find magnetic induction
Consider the static field configuration shown in the image. There are three layers: 0 = vacuum, 1 = magneto-optic fluid and 2 = covering shell. Each of these layers have their own permittivity and permeability (ε_i,μ_i) (isotrope). A uniform electric field H_0 = H_0/sqrt(2) * (e_x + e_y) is...- phys194
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

How Does Magnetic Force Affect a Falling Coil's Velocity and Kinetic Energy?
Consider a coil perpendicular to the ground falling with gravity. Under it, there is a magnetic field also perpendicular to the coil. When the coil starts penetrating the magnetic field there will be an induced current and therefore a magnetic force upwards. This magnetic force will reduce...- jaumzaum
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Force Magnetic Magnetic force Work
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

B Behavior of compasses AFTER the magnetic pole
So I know that a compass points to the south magnetic pole, that is near the north geographic pole. Let's consider the Earth to be a magnetized bar with all 4 poles aligned (for didactic purposes). The compass will try to "follow" the south magnetic pole, so, if I am in the Equator for example...- jaumzaum
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
G
How to get the magnetic moment for this loop?
About this figure, the current in the opposite wires are parallel (and not anti-parallel). So, for instance for the first option the torque is zero; but I wanted to know what is the magnetic moment of this loop. Since I rely only on formula I've have no idea how to compute for this one.- Gourab_chill
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Particle motion in a magnetic field
The equation of motion can be integrated w.r.t. ##t## since ##\frac{d}{dt} (\mathbf{r} \times \mathbf{B}) = \dot{\mathbf{r}} \times \mathbf{B} + \mathbf{0}## $$\int (q\dot{\mathbf{r}} \times \mathbf{B} + m\mathbf{g}) dt = \int m\ddot{\mathbf{r}}(t) dt$$ $$\frac{q}{m} \mathbf{r} \times \mathbf{B}...- etotheipi
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I'm not getting the curl of vector potential equal to magnetic field
In this image of Introduction to Electrodynamics by Griffiths . we have calculated the vector potential as ##\mathbf A = \frac{\mu_0 ~n~I}{2}s \hat{\phi}##. I tried taking its curl but didn't get ##\mathbf B = \mu_0~n~I \hat{z}##. In this thread, I have calculated it like this ...- Adesh
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Home experiment - 'seeing' magnetic lines of force?
Thought of doing this one years ago! Basically, I want to 'see' the magnetic force lines that surround a conductor when energized (with an alternating current). I appreciate that what I will see (or at least I am hoping to see) is the pattern formed by the iron dust in response the the field...- LentilSoup7
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Experiment Force Home Lines Magnetic
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-

Magnetic field due to the current flowing in a bent wire
Hello, in this problem I'm supposed to calculate de magnetic field due to a bent wire at any point of the x-axis after the bending of the wires. It is obvious that the part of the wire that is parallel to the x-axis makes no contribution to the field so we can focus on the other part of the...- Elder1994
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Quantum motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field
Once I know the Hamiltonian, I know to take the determinant ##\left| \vec H-\lambda \vec I \right| = 0 ## and solve for ##\lambda## which are the eigenvalues/eigenenergies. My problem is, I'm unsure how to formulate the Hamiltonian. Is my potential ##U(r)## my scalar field ##\phi##? I've seen...- EightBells
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Mastering Physics Homework about Magnetic field
Magnetic fields are sometimes measured by balancing magnetic forces against known mechanical forces. Your task is to measure the strength of a horizontal magnetic field using a 12-cm-long rigid metal rod that hangs from two nonmagnetic springs, one at each end, with spring constants 1.3 N/m ...- eedftt
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
W
Why a steel plate can shield magnetic field?
If I put a very long steel plate above a coil with DC, the magnetic field above the plate will decrease because of the shielding of the steel plate. However, from the perspective of magnetci domain, some domains will be magnetized to turn to the direction of the magnetic field from the coil...- w9537
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Electromagnetism