You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Motion: Definition and 1000 Discussions
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position over time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and time. The motion of a body is observed by attaching a frame of reference to an observer and measuring the change in position of the body relative to that frame with change in time. The branch of physics describing the motion of objects without reference to its cause is kinematics; the branch studying forces and their effect on motion is dynamics.
If an object is not changing relatively to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be at rest, motionless, immobile, stationary, or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. As there is no absolute frame of reference, absolute motion cannot be determined. Thus, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion.Motion applies to various physical systems: to objects, bodies, matter particles, matter fields, radiation, radiation fields, radiation particles, curvature, and space-time. One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries. So, the term motion, in general, signifies a continuous change in the positions or configuration of a physical system in space. For example, one can talk about the motion of a wave or about the motion of a quantum particle, where the configuration consists of probabilities of occupying specific positions.
The main quantity that measures the motion of a body is momentum. An object's momentum increases with the object's mass and with its velocity. The total momentum of all objects in an isolated system (one not affected by external forces) does not change with time, as described by the law of conservation of momentum. An object's motion, and thus its momentum, cannot change unless a force acts on the body.
View More On Wikipedia.org
If an object is not changing relatively to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be at rest, motionless, immobile, stationary, or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. As there is no absolute frame of reference, absolute motion cannot be determined. Thus, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion.Motion applies to various physical systems: to objects, bodies, matter particles, matter fields, radiation, radiation fields, radiation particles, curvature, and space-time. One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries. So, the term motion, in general, signifies a continuous change in the positions or configuration of a physical system in space. For example, one can talk about the motion of a wave or about the motion of a quantum particle, where the configuration consists of probabilities of occupying specific positions.
The main quantity that measures the motion of a body is momentum. An object's momentum increases with the object's mass and with its velocity. The total momentum of all objects in an isolated system (one not affected by external forces) does not change with time, as described by the law of conservation of momentum. An object's motion, and thus its momentum, cannot change unless a force acts on the body.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
P
Induced EMF due to motion of a wire perpendicular to a magnetic field
This question appeared in a university entrance exam.Basically, if magnetic flux passing through a surface of a loop changes over time ,only then e.m.f will be induced to that loop.But here only a straight line is used and there's no chance of forming any area.So by definition there's no chance...- phymath7
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Is simple harmonic motion also a pure translatory motion?
Is simple harmonic motion also a pure translatory motion?"A rigid body moves in pure translation if each particle of the body undergoes the same displacement as every other particle in any given time interval" [Halliday and Resnick, Physics].If not,then how does shm deviate from this definition> -

Planar Motion — Maximum acceleration of a crate up an incline before tipping over backwards
Correct answer is (b) 0,620 ms2 My attempt: FBD Equation 1. ∑Fx=0=−ma−Wsin(15)+f N=Wcos15 f=Nμs=379,03N Equation 1. ma=f−Wsin15 15a=379,03−203,1 a=2,20ms2 Equation 2. ∑MG=0=−Nx+f1,5 x=0,75m- Vladimir_Kitanov
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Acceleration Incline Maximum Motion
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Acceleration of system related to rolling motion and pulley
There is no friction mentioned by the question so I assume the plane is frictionless but can the sphere roll without slipping if there is no friction? This is my attempt: Equation of translation motion of object A (assuming A moves upwards): TA - WA sin θ = mA . aCOM (A) TA = mA . aCOM (A) + WA...- songoku
- Thread
- Replies: 35
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Can you explain the correct way to choose axes for circular motion analysis?
Haii, I don't understand why I need to choose my n-t components in the direction of a circular motion and can't just use them with the n-axis along the rope and the binormal perpendicular to the surface.- link223
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Analyzing Mass A's Direction of Motion
I am not very sure how I would be approach this. Obviously it is stated in which direction it's going where we see that mass A goes to the right, but how do I determine this stuff analytically.- link223
- Thread
- Replies: 32
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Motion in Cylindrical Coordinates
7:03 what is second component of a(theta)? this -> 2 * r' * (theta)' I understand everything except that.- Vladimir_Kitanov
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Solving a Circular Motion Problem - Expert Tips and Techniques
Could someone please help me solve this?- bloodlust_X
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

B Rolling Motion Test: Take the Challenge and Justify Your Answers
I am posting this to generate a parallel discussion to this ongoing thread. It seems that some participants in that thread have doubts and confusion about rolling motion that might be better addressed separately from the homework problem in question. It is a simple test of one's understanding... -
E
B Is All Motion Discrete or Continuous in QM?
We were discussing how much weight it would take to stop the mechanism from rotating in this thread: https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/weight-required-to-hang-straight-down-with-known-torque.1016470/#post-6646777 I wondered if there were actually a range of weights that would stop it...- erobz
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Continuous Discrete Motion Qm
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Motion Under Gravity: Physics Basics
.- GFREY
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
I Solving for the Motion of a Spring Pendulum
Given the pendulum setup below: Details: ##m## is the mass of the bob ## r ## is the instantaneous length of the spring ## \theta ## is the angle the bob makes w.r.t vertical ## I ## is the bobs mass moment of inertia about pivot ## l_o## is the free length of the spring. ##k## is the spring... -

I Will a spherical mass be set in motion by a spherical shell rotating around it?
In general relativity, rotation of mass gives rise to framedraging effects, just like linear motion does, because of the off-diagonal components in the mass-energy-momentum tensor. So around Bonnor beams there is framedragging, as well around a rotating mass. Now imagine a spherical rotating...- JandeWandelaar
- Thread
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
I Brownian motion and continuity
It is said often that in 1905 Einstein “mathematically proved” the existence of atoms. More precisely, he worked out a mathematical atomic model to explain the random motion of granules in water (Brownian motion). According to that mathematical model, if the atoms were infinitely small and...- DesertFox
- Thread
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
C
I Velocity for uniform circular motion
Hello everyone, I've been studying centripetal and centrifugal acceleration and derivation of their magnitude. I noticed in one of Walter Lewin's lectures that the velocity is written as both a vector and an arc length which is confusing to me. When velocity is written as a vector, it has a...- Chenkel
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
G
Projectile motion when kicking a ball that lands on an upward slope
We know x = R =max range (28m) on level ground. Need to find v()^2. Subbing y=0 into (1) above, get v(0)^2 = (gR^2/)/(2*cos (theta)^2 * tan (theta). ... (2) This didn't seem right, since this means v(0)^2 is a negative number ... maybe my orientation or algebra wrong? Anyway, didn't see...- gjh
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Integrating motion equation to derive displacement
##\frac{dx}{dt} = \frac{dx_i}{dt} + \frac{d^2x}{dt^2}t## Multiplying dt on both sides and integrating we have ##\int_{x_f}^{x_i} dx = \int_{0}^{v_i t} dx_i + \int_{0}^{at} dvt## so ##x_f - x_i = v_it + at^2##, which is not right Where did I go wrong? I understand that if we substitute a for...- annamal
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Deviation of Plumb Bob In Uniform Circular Motion
I started by making my coordinate system so that the x-axis aligned with the radius of the circle at a certain latitude L and the positive direction was facing away from the center of the circle, and the y-axis was parallel to the vertical axis of the Earth. Then, I wrote the equations for the...- mopit_011
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
U
Golf Ball Projectile Motion Problem -- Solved
26.6m/s = v0 36.5º = θ g = 9.81m/s^2 A) Find Range: (v0^2)/g *sin2θ = (26.6^2)/9.81 * sin2(36.5) = 89.99 I double-checked with the other Range equation (2v0*cosθ * (v0sinθ)/g) so I know I'm doing something wrong. Please help! Thank you edit: A) Correct answer is 69.0- Undeterred247
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Projectile Motion of motorcyclist
I assumed the cyclist was going 60-kph. Then worked backwards as shown above to calculate the deceleration in the x direction and then the time to decelerate to a stop at 39 m. Then used this time to calculate the initial speed if cyclist thrown 39 m, which was 8.4 m/s. But if he was going...- gjh
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Heavy mass vs light mass in circular motion
i think that the light sphere will go up higher(will have bigger acceleration) because there has to be a balance between the mass and the acceleration as long as the force is the same, for example if you push a heavy object and with the same force pushed another light object the light object...- technotux
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Equations of motion for the Schwarzschild metric (nonlinear PDE)
I'm working through some things with general relativity, and am trying to solve for my equations of motion from the Schwarzschild Metric. I'm new to nonlinear pde, so am not really sure what things to try. I have 2 out of my 3 equations, for t and r (theta taken to be constant). At first glance...- BiGyElLoWhAt
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Differential Equations
-
S
Misc. Are there alternatives to a Stewart platform that have more lateral motion?
As per the short description, really! I'm working on a project which involves a stewart platform: to give angles and vertical movement, but the main application of my design requires a large degree of lateral movement, about 4 times more than the dimensions of the top platform itself. Before...- some bloke
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: DIY Projects
-
T
A Brownian Motion (Langevin equation) correlation function
So the Langevin equation of Brownian motion is a stochastic differential equation defined as $$m {d \textbf{v} \over{dt} } = - \lambda \textbf{v} + \eta(t)$$ where the noise function eta has correlation function $$\langle \eta_i(t) \eta_j(t') \rangle=2 \lambda k_B T \delta_{ij} \delta(t -...- Tim667
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

B What is the relationship between force and distance in planetary motion?
https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_09.html 9-7 "From this figure we see that the horizontal component of the force is related to the complete force in the same manner as the horizontal distance x is to the complete hypotenuse r, because the two triangles are similar. Also, if x is...- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

B Analysis vs arithmetic approach to solving motion
https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_10.html https://www.feynmanlectures.caltech.edu/I_09.html Using Mathematical approach we can describe the motion of a falling body whose gravity is 32 m/s^2. Analysis shows that this is simply ##s-s_0=ut+1/2at^2##. Similarly we can describe the motion of...- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Mechanics
-
A
I Constant Velocity Motion in Relativity: Radiation Effects?
Does relativity imply that everything that goes at a constant velocity must not emit radiation of any kind?- accdd
- Thread
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
C
Velocity Formulas for Projectile Motion
Hi, so I solved this using energy. I also tried solving this using kinematic equations. The issue I am running into s for calculating the Vy of the problem. I am able to find the time it takes the rock to fall using d=(1/2)gt^2. Then, I considered two different ways of going about finding the...- chromechris1
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Circular motion to projectile motion
So first I found the velocity of the ball at the bottom of the swing from the force equations, which I got to be 4.9 m/s and this is only in the x-direction. Then using the projectile motion for delta y I found time, which is 0.2s. Then using that time I found the delta x to be 0.98m. I just...- ChetBarkley
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
I Relative Motion vs. 'Relative' Acceleration: Twin 1 & 2
Given the relativity concept between twin 1 and twin 2 what is the difference between relative motion and 'relative' acceleration? Are not either twin experiencing the differential between them as a consequence of acceleration. When twin 1 instigates motion relative to twin 2, a moving carriage...- Martyn Arthur
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
Finding the differential equation of motion
Summary:: Differential equation of motion, parabola Hi. I've tried resolve this problem but I have two doubts. The first is about the differential equation of motion because I can't simplify it to the form y" + a*y' + b*y = F(t). I'm not sure if what I got is right. My second doubt is that I...- dbeckam
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

Simple Ramp motion problem, but going full vector mode
Known: 1) The mass of the ball is ##m## (constant ##\frac{dm}{dt} = 0##) 2) ##v(0) = v_{0}## 3) Air drag force magnitude ##| \vec F_{D} | = B \cdot | \vec v(t) |## (##B \in R##) 4) The ramp is frictionless. 5) The magnitude of Earth's acceleration = ##g## I'm not sure if θ is known or not, and...- babaliaris
- Thread
- Replies: 29
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Comp Sci Confusion on motion estimation block diagram-MPEG video compression-:
My doubts are as follows-: -> Why frame n is not segmented to blocks? -> Why no inputs from (n-1) side for block matching? -> What do we do in prediction error coding? Source-: https://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/AV0506/s0561282.pdf I have read this many times but that...- shivajikobardan
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-

MHB Confusion on motion estimation block diagram-MPEG video compression-:
https://lh4.googleusercontent.com/g6wQjnQ6p3IVt86-_kwnNVwyOb_iUxUXWChyf0XZR5PO17uOnPbNhCxdpfUSScvU8sAR8Al2FNRMoeMEqLUUuJsvGOSnpFO94tutB2h-927rxVYRDUGzi-JF9FYs9hKivGdCvrAP My doubts are as follows-: -> Why frame n is not segmented to blocks? -> Why no inputs from (n-1) side for block matching...- shivajikobardan
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Programming and Computer Science
-

I Measurement of charge in motion
In Purcell's E&M Section5.3 "Measurement of charge in motion", he said when a charge is in motion, the force on test charges may not be in the direction of radius vector r. And in next paragraph, he defined Q by averaging over all directions. However, he just measured the radial component of...- janjan
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Find the acceleration in circular motion
Hello , First of all , I am still new to circular motion or any motions in general and still relatively learning so please bear with me. 1 . The direction of the tangential acceleration is parallel to the net velocity and that of radial of perpendicular to the velocity. So the direction of net...- theerenwithther
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B Gravitational acceleration in circular motion
Hi guys, I have a question that is simple but I do not know how to answer that. It is the following, where does the acceleration of 9,8 meters per second squared go when We're dealing with uniform circular motion? I know that We have the centripetal acceleration that is a vector change, but the...- physicsmagician
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-
V
Direction of motion of points on a rope as a wave travels
The second diagram is my attempt at the solution, in which the dotted part is the pulse in the rope a very small interval of time after ##t=0##. Point A should be at rest since we know wave is moving towards right and point A on the rope becomes a part of initial horizontal part of the string a...- vcsharp2003
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Magnetic field's effect on a charged particle's motion
I actually have no idea how to begin. Thanks for help 😊 -
S
Motion in two dimensions: Launching up an incline
But it seems to get too complex and am not sure whether it is correct.. my solution got a bit messy + incorrect Thanks in advance!- simphys
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Motion of an Object: Displacement & Average Velocity
An object starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s2 for 4.0 s. Its velocity remains constant for 7.0 s, and it finally comes to rest with uniform deceleration after another 5.0 s. Find the following: a. the displacement for each stage of the motion b. the average velocity over the whole time...- Stewkatt
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Seeking the Equation of Motion for a charged mass attached to a spring
I'm surprised that this question only occurred to me recently. If a have an electrically charged mass attached to a spring and set it oscillating, the resulting production of electromagnetic waves must cause a kind of "friction", a force resisting the motion of the charged mass, so that its...- snoopies622
- Thread
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
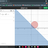
Plotting the graph of Friction Force vs. time (Laws of motion)
F.B.D Of first block (I have shown only the horizontal Forces) f1(max) = μ (1kg)(g) = 0.5 * 10 = 5N F.B.D Of the second Block f2(max) = μ (3kg)(g) = 15N Now the string will become taut and the tension will start acting when f = t = 5N But for 0<f<5N there will be no motion between the 1 kg...- SpectraPhy09
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Reasoning/evaluation: Free fall motion with constant acceleration
My guess is that I could compare it to the time interval of the free fall motion(stage2). Would that be enough to let it make ‘sense’? As we know that stage 1 has an acceleration of 16m/s^2 and free fall one of 9.81m/s^2. Then.. is it sufficient to reason that the time needed to complete stage...- simphys
- Thread
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Velocity along the cylinder axis
Since the question says that "velocity along the cylinder axis" and "magnetic field perpendicular to the cylinder axis". So cross product of velocity and magnetic field becomes their magnitude. ##\vec v\times \vec B=||v|| \\ ||B||## So ##\vec F=qvB## ##mg=qv\frac{\mu_0 nI}{4\pi r}## At first...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Find force on a particle at time t
My attempt : ##\frac{\vec Ft^2}{2}=m\vec s## ##s=\frac{Ft^2}{2m}## ##P=\frac{W}{t}## ##k=\frac{\vec F\cdot \vec s}{t}## ##k=\frac{F^2t^2}{2mt}## ##k=\frac{F^2t}{2m}## ##F=\sqrt{\frac{2mk}{t}}## But there was an option which was ##2\sqrt{\frac{mk}{t}}##. And my assumption was that it was... -

Find focal length of electron for a parabolic motion
Here I was going to use ##\int \vec F \cdot d\vec l = \frac{1}{2}mu^2## What I got that is ##l=\frac{mu^2}{2eE}##. Here the question is what is ##l## (I took ##x## while doing the work but here I used ##l## instead of ##x##)? I was assuming that it's ##x## since I am calculating work in the...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How to find integrals of motion for a particle on a surface?
I have no idea where to even start with this, please help. I barely even know what integral of motion means. -

Solving Motion Equations with Integration
I'm not sure where to start, when I tired using integration of the initial equation to get pos(t)=-.65t^2 i + .13t^2 j + 14ti +13tj but after separating each component, i and j, and setting j equal to zero I got 0 or -100 seconds which doesn't seem like a reasonable answer.- runningphysics
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How Does Acceleration Affect Velocity in 1D Motion?
##v=\frac12 *1*4+\frac12*1*4= 4 m/s## but the answer is wrong.- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help