You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Motion: Definition and 1000 Discussions
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position over time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and time. The motion of a body is observed by attaching a frame of reference to an observer and measuring the change in position of the body relative to that frame with change in time. The branch of physics describing the motion of objects without reference to its cause is kinematics; the branch studying forces and their effect on motion is dynamics.
If an object is not changing relatively to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be at rest, motionless, immobile, stationary, or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. As there is no absolute frame of reference, absolute motion cannot be determined. Thus, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion.Motion applies to various physical systems: to objects, bodies, matter particles, matter fields, radiation, radiation fields, radiation particles, curvature, and space-time. One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries. So, the term motion, in general, signifies a continuous change in the positions or configuration of a physical system in space. For example, one can talk about the motion of a wave or about the motion of a quantum particle, where the configuration consists of probabilities of occupying specific positions.
The main quantity that measures the motion of a body is momentum. An object's momentum increases with the object's mass and with its velocity. The total momentum of all objects in an isolated system (one not affected by external forces) does not change with time, as described by the law of conservation of momentum. An object's motion, and thus its momentum, cannot change unless a force acts on the body.
View More On Wikipedia.org
If an object is not changing relatively to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be at rest, motionless, immobile, stationary, or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. As there is no absolute frame of reference, absolute motion cannot be determined. Thus, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion.Motion applies to various physical systems: to objects, bodies, matter particles, matter fields, radiation, radiation fields, radiation particles, curvature, and space-time. One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries. So, the term motion, in general, signifies a continuous change in the positions or configuration of a physical system in space. For example, one can talk about the motion of a wave or about the motion of a quantum particle, where the configuration consists of probabilities of occupying specific positions.
The main quantity that measures the motion of a body is momentum. An object's momentum increases with the object's mass and with its velocity. The total momentum of all objects in an isolated system (one not affected by external forces) does not change with time, as described by the law of conservation of momentum. An object's motion, and thus its momentum, cannot change unless a force acts on the body.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Overcoming Difficult 2D Motion Problems: My Journey to Advanced Physics
Ive been reading University physics by roger freedman, I’m on section 3 motion in 2d. I can solve most of the problems ag the end of the chapter, or at least understand the solutions. But there is a small extra section called challenge problems. There’s only 3 but I found them very difficult...- bigmike94
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-

B About Second equation of motion
I was wondering how the second equation of motion produces negative displacements ##s= ut+\frac 12 at^2## . Is ##\frac12 at^2## kind of distance operator?- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Circular Motion Problem -- Ball on a String Spinning in a Vertical Circle
#F= m\frac{v^2}{r} = mw^{2}r# #m=5# #r=0.9# #F= 5\frac{v^2}{0.9} = (0.9)5w^{2}# #5\frac{v^2}{0.9} = (0.9)5w^{2}# #\frac{v^2}{0.9} = (0.9)w^{2}# #v=0.9w# then I get stuck cause I have both unknowns in one equations (i bet it has something to do with the question’s use of “minimum” but I...- Al-Layth
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A Does gravity affect Brownian Motion?
I know passive diffusion rates behave differently on the International Space Station relative to Earth (video of a contained flame experiment burning up there.) However, does the random walk of pollen particles etc. have slowed velocity in comparison to that on Earth? Has been bugging me for a...- dedocta
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Brownian motion Gravity Motion
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

Kinematic Equations in Projectile Motion (this approach is not working)
Givens: Vyi=12.5 m/s Vyf=-12.5 m/s (at the same horizontal level) ay=-9.81 m/s^2 Δy= zero m (as the displacement on the y-axis, when the projectile reaches the same horizontal level, is zero m) Δt=? When I use Δy=[(vyi+vyf)/2]*Δt I get the time as undefined. Δt= 2Δy/(vyi+vyf) = 2*0 m/(12.5...- GiantYoda
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Positive Charges: Explaining Motion Despite Net Force = 0
in a cours of electrostatic when we have a positive charge and we bring another one (also postitive)we have to do work and apply a force that equals the force of repultion over the distance which seems weird because if we do that the net force will be equal to 0 and the charge will not move can...- samy4408
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

How Does Rocket Ejection Mass Affect Its Velocity in Space?
Consider a rocket with mass ##m## in space is going to move forward. In order to do so, it needs to eject mass backwards. Let the mass that is ejected has velocity ##u## relative to the rocket. What is the equation for the final velocity? It is said that after ##dt## second, the rocket will...- Father_Ing
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
I Angular momentum of an atom within a rigid body in motion
Considering an atom within a rigid body, does the angular momentum of an electron within the atom vary when the body is put in motion? My intuition is that, whether considered in a classical sense or quantum sense, the speed of a given electron in its motion within an atom will be constant and...- james fairclear
- Thread
- Replies: 61
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Car that undergoes non-uniform circular motion
In the solution manual, it says that: the resultant of friction force is ##<= kmg##, hence $$m\sqrt{\omega_t^2 + (\frac {v^2} {R})^2} <= kmg$$ and from this equation, we will get $$v^2 <= R \sqrt{(kg)^2 -\omega_t^2}$$ which will make ##v_{max}^2= R \sqrt{(kg)^2 -\omega_t^2}## Finally, they...- Father_Ing
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
I Conversion of Fluid Rotational Force to Rocking Motion
Does anyone know how to convert the parameters within constraints to equate rocking motion from fluid being mixed through consistent shaking? What I am given: Centrifugal Force Calculations: mass = 0.25 kg angular velocity = 12.57 rad/s radius = 0.045 m What is known about the bag of fluid on...- akwok
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fluid Force Motion Rotational
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
A
B Newton's second law of motion -- Why is it F=m*a and not F=m+a?
Why F=m*a i.e product or multiplication and not F=m+a? i.e addition or summation?- akerkarprashant
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
K
A Cause of upward motion of a nutating top
The locus of the rotational axis of a symmetrical rotating top with a fixed base is shown. This shows a nutation bounded by two circles. What is the intuitive explanation as to why the top axis turns upwards at the lower circle and moves up? ( I understand the circular precession caused by... -

Projectile Motion Experiment: Results Too High?
Hello everyone, I have a homework about projectile motion experiment and I threw small ball over the table and ball did projectile motion at the end of the table and ı recording this motion on motion tracker and motion tracker gave me acceleration of y component of ball as 14.02 m/s^2. But it...- burakyildiz
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Finding Spring Constant When Given Amplitude, Time, and Mass
I averaged the masses and times (which i took the time given and divided by 10 because in the problem it says you measure the time it takes to complete 10 oscillations) then plugged them directly into the T=(2(pi)((m/k)^1/2) and got the wrong answer. This is really confusing me because I don't...- physicsneedslabs
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
I Confused about the axis of rotation in rotational motion w/o slipping
I'm now learning about rotational motion without slipping and it's really hurting my brain to think about. Imagine a cylinder rotating on a flat plane. I can accept that there is both translational and rotational motion. For example, a given point on the circumference of the cylinder follows a... -
L
An object oscillating in simple harmonic motion
Since it passes through the origin every ##3.6s## the period is ##T=3.6s## hence ##\omega=\frac{2\pi}{\omega}=\frac{2\pi}{3.6}\frac{rad}{s}## thus ##A=\frac{v_{max}}{\omega}=\frac{1.2}{\frac{2\pi}{3.6}}m\simeq 0.69m## and ##a_{max}=\omega^2 A=(\frac{2\pi}{T})^2 A=(\frac{2\pi}{3.6})^2 \cdot...- lorenz0
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Engineering Motion equation and transfer function of mass on a conveyor
Denote wheel turning angle as theta--> Induced EFM (Em)=Kb*Theta_dot. Voltages on the wheel: R*i= V - Em Moments on engine's axis: Kt*i-C*a + a (m+M)*x_double_dot=0 (As Jm negligible). From here I would find another equation to have x and theta expressing each other, but i think I'm...- alv13
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-

Another Doubt From Halliday Resnick Krane -- Puck on a string in circular motion
Hello! This is a problem from Halliday Resnick Krane (Chapter 4: Problem #15). “A puck is moving in a circle of radius r0 with a constant speed v0 on a level frictionless table. A string is attached to the puck, which holds it in the circle; the string passes through a frictionless hole and is...- vibha_ganji
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
B Resultant force in vertical circular motion
Suppose we have a vertical circular motion with gravity according to the image below. In the leftmost and rightmost positions the resultant force is pointing diagonally down. Isn't the resultant force supposed to be pointing at the center at all times in a circular motion? What am I getting...- Goliatbagge
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Mechanics
-
H
What is the meaning of work done for non-uniform circular motion?
This is my solution ,and I just use the definition .But I still feel unclear about the concept of non-conservative force.$$ W = F x = 30N (\frac{1}{2}\pi r ) = 56.2 J $$ $$ E_{system} = \Delta K + \Delta U = W $$ $$ (K_{f}- K(i))+(U(f)-U(i)) = W $$ $$ (\frac{1}{2} *m{V_{f}}^2...- hhjjy
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion
Would we assume that the deceleration of both instance are the same?- ayans2495
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Forces and laws of motion -- Big gorilla hanging from two vines
About 50 years ago, the San Diego Zoo, in California, had the largest gorilla on Earth: its mass was about 3.10 × 102 kg. Suppose a gorilla with this mass hangs from two vines, each of which makes an angle of 30.0° with the vertical. Draw a free-body diagram showing the various forces, and find...- HiReinhardt
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Forces Laws Laws of motion Motion
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
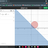
Motion in 1D-Graphs: Is Option D Correct?
I think Option C should be correct since the body has two velocities in the same position which is not possible. They even didn't show an arrow that could tell it has which velocity at its starting point and at the ending point But the given and in my textbook is Option d ( It can have an error...- SpectraPhy09
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Newton's laws of motion -- Force of gravity on a skydiver
I think you would do force of gravity= mass x acceleration acceleration of gravity= 9.8 m/s mass 75 kg 75kg x 9.8 m/s =735 N i don't know if that's right but i have no idea how to calculate it after he lands, any help would be greatly appreciated!- kara123
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A particle motion problem in the x-y plane with constant acceleration
I have attempted but I don’t get anywhere.- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
How to calculate differential work done by a force in circular motion?
My question is, is this correct, and if so, why the minus sign?- zenterix
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

What kind of motion is this? (bicycle velocity vectors)
How the heck the bicycle reach from point A to point B with that velocity vector directions?- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Periodic boundary conditions -> Shouldn't supports hinder all motion?
Hello everyone, I am currently trying to understand periodic boundary conditions for the mechanical investigation of mechanical properties of a RVE. I found a good video explaining the theory behind it: But something is unclear to me: At the above linked time step, the individual conical...- NewStuff
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

B Why doesn't a body accelerate upward when a force is applied?
When we apply a force to throw a body upward why doesn’t it accelerate in upward direction. I think the answer is continuous force of gravity slowing it down. So it is de accelerating from the moment it’s released. But recently we have applied a force so it should accelerate ?- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Mechanics
-

B Independence of vertical and horizontal motion
It says when the ball is shot the can is released and they both hit each other at the same height ie they travel same distance down. But that is only possible when the ball starts it’s downward journey the same time as the can starts it’s own. Shooting a ball upward direction will give it some...- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 46
- Forum: Mechanics
-
A
I Motion of a charged particle -- Changes in KE and PE?
If a charged particle moves through a potential difference, it gains kinetic energy but does it also lose potential energy? When I accelerate a particle and then I "free it", what happen to its potential energy if the total energy should be conserved?- aaronll
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Find the equation of motion using the Lagrangian for this Atwood machine
My understanding of the system from the image (which was given in book) I could see there's 3 tension in 2 body. Even I had seen 2 tension in a body. It was little bit confusing to me. I could find tension in Lagrangian from right side. But left side was confusing to me...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Find equation of motion of an inclined plane when there's friction
It's the body. So there's friction on that plane and there's tension also. $$L=\frac{1}{2}m_1\dot{x}^2+\frac{1}{2}m_2\dot{x}^2-m_2g(l-x)-m_1gx\sin\theta$$ $$f=\mu N=-\mu m_1 g\dot{x}\cos\theta$$ I had found the frictional force's equation from [the...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Relationship between horizontal range and angle of launch
I would like to conduct an experiment asking the question "how does the angle at which a projectile is launched vary with respect to the horizontal range it covers?" Ultimately, I'd like to prove that the horizontal range is directly proportional to sin(2(theta)). This will be done with the aid...- ayans2495
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
I Base Motion and Vertical Beam - Basic Reaction Forces?
So I am trying to understand how to estimate the amount of deflection [D] the vertical beam shown above would experience if the base it is attached to is accelerating at a constant acceleration [a] of 9.81 m/s. I assume the Force [F] would be equal to weight of the vertical beam (mass x...- sabz333
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

1-D Motion, calculating final velocity
Hello! I have done this problem : vf^2 = (4.0x10^5)^2 + 2(6.0x10^12)(5x10^-3) so vf= sqrt((4.0x10^5)^2 + 2(6.0x10^12)(5x10^-3)) I get vf = 4.7 x 10^5 m/s However, the textbook solutions says vf = 8.7x10^5 m/s. Where did I go wrong? Thank you for any help! :)- mncyapntsi
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Motion of a Particle: Solutions & Examples
This is jut an example to illustrate my doubt. I don't know how to obtain the tracjectory given only the acceleration in this format. I realized that if i can show that there is an constat vector 'a' that satisfy a•r=constant, than the motion would be on the surface of a cone. So i tried to make...- Einstenio
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Classical Mechanics - Motion of a particle
Show that a point with acceleration given by: a=c*((dr/dt)×r)/|r|3 where c is a constant, moves on the surface of a cone. This is jut an example to illustrate my doubt. I don't know how to obtain the tracjectory given only the acceleration in this format. I realized that if i can show that...- Einstenio
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
C
B E.P.E. -> ? when 2 masses are attached to a spring
Two masses m and M are attached to a compressed spring. When the spring decompresses, the masses won't be pushed off the spring. What will happen to the masses and the entire system? By conservation of energy, the elastic potential energy of the spring will convert into kinetic energy, but which... -

Motion - How do you find the time in the air of an object
Hi! I am really stuck on the concept, wouldn't we not have enough variables? I tried equation the equation for the y of the object to the slope of the hill, but I am missing several variables. Any help is greatly appreciated :) thanks!- mncyapntsi
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Air Motion Motion analysis Time
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How to translate force into upward hinging motion between two panels?
Pictured below are two hinged panels that can rotate upward to form an upside-down V. In position 1, the panels are lying flat. In position 2, the panels have folded together and the joined edge is raised up. Normally, in order to actuate this hinging motion, one would need to manually lift the...- mmcnaught831
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

I Two axis motion for any vehicle
This question I have been thinking for some time. 1. For an Aircraft we have 4 types of motion. Yaw, Pitch, Roll and Forward Velocity. 2. For a Locomotive, we can say there are only Forward Velocity. No other axis of motion. 3. For a Car, we have the Forward Velocity and Yaw motion (steering...- Anand Sivaram
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Mechanics
-
S
MHB What is the maximum distance of P from point O during the motion?
A particle moves on a straight line. It starts at a point O on the line and returns to O 100 s later. The velocity of P is v m/s at time t s after leaving O where v= 0.000t^3- 0.015t^2 +0.5t. 1) Find the values of v at the times for which the acceleration of P is zero I got when t= 21.1s, V=...- Shah 72
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Line Motion Straight line
- Replies: 10
- Forum: General Math
-

Tangential & Normal acceleration in Circular Motion
- Shreya
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A Motion of a spring that has mass
Hello! I was trying to find the equations of motion for a spring with uniform distribution of mass (uniform just in t=0, because after a while the distribution will be non-uniform). I tried to attack this problem first in the discrete (non-continuous) way: "Consider N springs with elastic...- jaumzaum
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
T
Circular motion of a mass on a string on an inclined plane
(I drew motion in the opposite direction so the object would rotate trigonometrically but it should be the same thing) I have just finished the Kinetic Energy and Work chapter in my course and this is the last problem from the problem set. I have not worked many problems with the Work-Kinetic...- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Newton's First law of motion -- Boy jumping vertically on a moving train
I'm not sure if my answer is correct but I think the answer is false. Thank you for your help :) -sun1108- Mikasun1108
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
B Is Newton's first law of motion applicable when walking?
Is Newton's first law of motion applicable when walking?- Einstein60
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanics
-

B Exploring Electron Motion in Quantum Mechanics
I had two questions in the field of physics: We know that in quantum mechanics there is an electron in a certain distance from the distance to the nucleus as a cloud or a cover. But is motion for the cloud defined by the electron moving around the nucleus? And the main question is, can the...- ZIKA99
- Thread
- Replies: 29
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
C
I Angular Movement and Spiralling Motion
Hello, I am currently working on a computer program to move on object undergoing circular motion in a spiral of decreasing radius. I hope this is illustrated clearly below (forgive me but it is a sketch and thus not precise in scale): The scenario is as follows: 1. The object starts angular...- Cato11
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Classical Physics