You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Motion: Definition and 1000 Discussions
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position over time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and time. The motion of a body is observed by attaching a frame of reference to an observer and measuring the change in position of the body relative to that frame with change in time. The branch of physics describing the motion of objects without reference to its cause is kinematics; the branch studying forces and their effect on motion is dynamics.
If an object is not changing relatively to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be at rest, motionless, immobile, stationary, or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. As there is no absolute frame of reference, absolute motion cannot be determined. Thus, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion.Motion applies to various physical systems: to objects, bodies, matter particles, matter fields, radiation, radiation fields, radiation particles, curvature, and space-time. One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries. So, the term motion, in general, signifies a continuous change in the positions or configuration of a physical system in space. For example, one can talk about the motion of a wave or about the motion of a quantum particle, where the configuration consists of probabilities of occupying specific positions.
The main quantity that measures the motion of a body is momentum. An object's momentum increases with the object's mass and with its velocity. The total momentum of all objects in an isolated system (one not affected by external forces) does not change with time, as described by the law of conservation of momentum. An object's motion, and thus its momentum, cannot change unless a force acts on the body.
View More On Wikipedia.org
If an object is not changing relatively to a given frame of reference, the object is said to be at rest, motionless, immobile, stationary, or to have a constant or time-invariant position with reference to its surroundings. As there is no absolute frame of reference, absolute motion cannot be determined. Thus, everything in the universe can be considered to be in motion.Motion applies to various physical systems: to objects, bodies, matter particles, matter fields, radiation, radiation fields, radiation particles, curvature, and space-time. One can also speak of motion of images, shapes, and boundaries. So, the term motion, in general, signifies a continuous change in the positions or configuration of a physical system in space. For example, one can talk about the motion of a wave or about the motion of a quantum particle, where the configuration consists of probabilities of occupying specific positions.
The main quantity that measures the motion of a body is momentum. An object's momentum increases with the object's mass and with its velocity. The total momentum of all objects in an isolated system (one not affected by external forces) does not change with time, as described by the law of conservation of momentum. An object's motion, and thus its momentum, cannot change unless a force acts on the body.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Motion of rotating rig, find the angle variation with control rod length
Summary:: We have a rotating arm, offset from the centre of rotation by a certain length, which is controlled by varying the length of a control rod. Need the angle of the rotating arm in terms of length of the rod. The blue line is a fixed column structure. CE and BD form the rotational... -

B Energy, Mass, Speed of Light: Can We Reach It?
Hello everyone! Let's say that you were to attempt to go as fast as possible on a spaceship with the mass of an average car in an absolute perfect vacuum. What I am wondering is, that if you were to reach a certain speed, and stop applying energy to this imagined spaceship, would the spaceship...- LawH
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

Circular motion and g forces in rollercoaster
I my attempt, I set the drop height to 20m and using conservation of energy, i calculated the speed at the bottom. Calculating centripetal acceleration, if the radius of the circle is less than 10m then the g force is greater than 5, if equal to 10m the velocity at the top is 0 and there is 0...- Erucibon
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Circular motion of a car on a banked road
f=(m v^2)/r- MIN JIN
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Car Circular Circular motion Motion
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Movement contraptions that inspired Newton's 2nd law of motion
Besides gravity that always works perpendicular to Earth and thus pulls apples from apple trees towards the ground, there must have been some sort of mid 17th century human made contraption, that used a constant force, produced to move objects with or without wheels, in a direction parallel to...- roineust
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
-
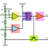
Vector Mechanics — Double Gear Rolling on a Rack
Hi! My first question: How does he get the equation ##\frac {x_A} {2πr_1} = -\frac {θ} {2π}## ?- Alexanddros81
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Why Does Projectile Motion Involve Zero X-Component Acceleration?
I intended to finish the question with the equation of linear motion with constant acceleration, but it didn't work out. And I have no idea about the t^3 and t^4 of the position. How can I find the x component of the acceleration at time 3.4 s ? Where is the acceleration rate?- jamiebean
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Projectile Motion — How far from the gun does the bullet land?
I don't know how to link the x-component and y-component together.- Tinkylo
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Slip stick motion and a glass harp (singing glasses)
-- fizzyfiz
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How can I draw a motion diagram?
I attached an image- bri_garcia11
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Finding motion where the acceleration depends on position and time
I have computed that the acceleration in my problem is a(t) = -gj - k/m(|r(t)| - L_0) * r(t)/|r(t)| Where a(t) is the acceleration vector, g is the gravitational acceleration, j is the unit vector in y-direction, k is the spring constant, m is the mass, r(t) is the position vector, |r(t)| is... -
S
Projectile motion on an inclined plane
a. I tried to "rotate" the inclined plane so the surface of the inclined plane becomes horizontal h = Vi sin θi . t - 1/2 g cos ∅ t2 and when it falls to the plane, y = 0 so: 0 = Vi sin θi . t - 1/2 g cos ∅ t2 t = (2 Vi sin θi) / (g cos ∅) Is this correct?b. Particle hits the plane vertically...- songoku
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Rotational Motion Problem with Varying Centripetal Force and Friction
Hello, I'm stuck in this rotational motion problem (advanced high school level). Source: Problems in General Physics- IE Irodov My attempt(s): First I tried using work done by the moment of friction (mgkR) and equated it with change in KE. I got the answer as ## \frac{R (\omega_0)^2}{8 \pi...- Pi-is-3
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Insights Why We Don’t Discuss Perpetual Motion Machines (PMM)
Continue reading...- russ_watters
- Thread
- Replies: 31
- Forum: General Engineering
-

A Puzzle Involving the Moon's Orbital Motion
This is a puzzle involving the orbit of the Moon around the Earth, based on the well-known story of Newton observing a falling apple and wondering if the same force that made the apple fall could also explain the motion of the Moon. The story goes that Newton considered the following: the...- PeterDonis
- Thread
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Mechanics
-
H
What is the inverse of the covariance operator in Brownian motion?
in fact the answer is given in the book (written by philippe Martin). we have $$ (\tau_1| A^{-1} | \tau_2) = 2D \ min(\tau_1 ,\tau_2) = 2D(\tau_1 \theta (\tau_2 -\tau_1)+\tau_2 \theta (\tau_1 -\tau_2))$$ So $$-1/2D \frac{d^2}{d\tau_1^2} (\tau_1| A^{-1} | \tau_2) = \delta( \tau_1 - \tau_2) $$... -
R
Elliptical motion: An object is moving at a constant speed?
I am confused why the acceleration doesn't point to the center of the ellipse or one of the focus, since it moves in circular motion. Shouldn't the acceleration be just in the radial direction- rashida564
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Motion in Electric and Magnetic Fields -- (Uni Level Dynamics)
I've attached my attempt at a solution below, I thought integrating it would be the best way to go but I'm just getting so confused and could use some help. This isn't my first attempt at a solution either I've been working on this for just under two hours now.- SianRR
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Perpetual Motion Idea: Is It Possible?
Hi all,Minimal math/physics background here, so bare with me. Imagine a smooth track or tube that tightly spirals downwards into smaller and smaller circles. Now imagine if a ball rolls down that spiral, gaining speed. At the bottom/end of the spiral the track/tube goes underneath the spiral...- jrm415
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Idea Motion Perpetual motion
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
P
Equation of Motion of a Particle acted on by a retarding force
I really can't figure out where to even start on this question- physconomics
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

How to know whether motion is simple harmonic motion or not?
I am reading "Coulomb and the evolution of physics and engineering in eighteenth-century France". There it is said in page 152 para 1 that "Coulomb found that within a very wide range, the torsion device oscillated in SHM". My questions are: (1) By just looking at the time period of the...- Beelzedad
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Motion involving drag force
Since given F = -kdx/dt so I equated mx'' = -kx' which gave x(t) = A + B exp(-kt/m) hence v(t) = (-kB/m) exp(-kt/m) and using v(0) = u, v(t) = u exp(-kt/m) then I...- tanaygupta2000
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Drag Drag force Force Motion
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
Derivation of the Equations of Motion for a System
Summary:: This is a system and we want to find the equations of motion. After some force-based attempts, I think that it would be easier to use some energy methods. Hi, I wanted to ask about deriving equations of motion by using the Lagrangian. The question is in the picture below. We are...- Master1022
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
L
Projectile motion of a two-point rigid body
I would like to patch some gaps in my physics background. For example, I've been trying to come up with the sollution to the following: I have a model rigid body made up of two mass points and a massless rod connecting them. I throw the body with initial velocity under some angle of elevation...- luinthoron
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Mechanics
-
Get all possible constants of motion given an explicit Hamiltonian
I do not understand the following sentence (particularly, the concept of extra symmetry): 'If all ##\alpha^i## are the same, then there is extra symmetry and corresponding constants of motion'. OK so let's find the Lagrangian; we know it has to have the form: $$L(q, \dot q) = T(q, \dot q) -...- JD_PM
- Thread
- Replies: 56
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
R
Question about the Signs of Rotational Motion
I got a confusion about the sings in the angular acceleration. When dealing with system of pulleys, how to define where is the positive and negative direction of the motion and will the choose of positive direction of angular acceleration will effect the positive direction of linear acceleration- rashida564
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Mechanics
-
T
Projectile Motion with Air Drag
Tell me now if this question is posted in the wrong place. This isn't a homework problem per se, it's just a question I need answered and I'm not sure how to answer it. If there is any information missing, chances are I know it and forgot to post it, so please ask if something is missing. I...- trumanf_
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Deriving Momentum From Newton's Second Law of Motion
Hello everyone I was hoping someone could shed some light on the following:- I am trying to derive the equation of Momentum from Newton's 2nd Law. What I know is the following:- I don't know how to get from Force = Mass * Acceleration TO Momentum = Mass * Velocity. I have attempted to...- tomtomtom1
- Thread
- Replies: 27
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Motion of 2 masses connected by a rod to a pendulum
I am not sure which other forces I should consider besides those 3. I cannot consider tensions due to the massless rod on the masses since those will not add up to zero.- Jenny Physics
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Using Noether's theorem to get a constant of motion
Noether's theorem tells us that an invariance of the Lagrangian yields a constant of motion. In this problem, that constant is: $$Q_v = p^a \Big( \frac{\partial q_a^{\lambda}}{\partial \lambda}\Big)_{\lambda = 0} + p^b \Big( \frac{\partial q_b^{\lambda}}{\partial \lambda}\Big)_{\lambda = 0}=...- JD_PM
- Thread
- Replies: 81
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
Simple Harmonic Motion Amplitude
Using A = x0, B = v0/ω I get ω = 4π, A = 1, B = 1/4π then converting to phase/magnitude form \sqrt{A^{2} + B^{^{2}}} = \alpha \sqrt{1^{2} + \left ( \frac{1}{4\pi }\right )^{^{2}}} = \alpha = \frac{1}{4\pi }\sqrt{16\pi^{2} +1} However the answer in the back of the book has α = 1 Is...- Teclis
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
Equation of motion of a simple pendulum
The equation of motion of a simple pendulum is: $$\ddot \theta + \frac{g}{l} \theta = 0$$ Our Physics professor told us: 'If you want to become a good Physicist you have to be able to analytically check your answers to see whether they make sense'. In class he took the limits of constant...- JD_PM
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Classical Mechanics "variable mass" linear motion problem in one dimention.
Please help please- cemtu
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Rotational motion: Number of revolutions before a flywheel comes to rest
Hi there I have been having a go at this question and I'm uncertain if my answer to part b) is valid? The problem is when I plug this into the calculator I get 6.379... revs however this doesn't make sense to me. 2*pi is roughly 6.28 radians so doing 4.061... rads / 6.28 rads = 0.647 revs...- Bolter
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Rotational motion and finding the moment of inertia
Here is the problem that I am finding difficult to answer I had tried using conservation of energy to do this question Where I know that the gravitational potential energy at the top of the slope equals to the sum of both the linear and rotational kinetic energy at the bottom of the slope...- Bolter
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Help with a problem about motion — bullet striking a block of wood
I first plugged my given values into m1v1+m2v2=(m1+m2)vf. (0.002)(600)+(5)(0)=((0.0020)+(5))vf vf=0.24 m/s Next, I plugged my given values into F=ma. ((0.002)+(5))(9.8) F=49.02 N Next, I plugged my given values into Fdeltat=mdeltav. deltat=mdeltav/F ((0.002)+(5))(0.24)/(49.02)... -

Engineering Sectional Lift/Moment coefficients w/ sinusoidal motion
I cannot figure out how to even start this.- spacepirat
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Coefficients Motion Sinusoidal
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
Deriving the Equation of Motion out of the Action
Exercise statement: Given the action (note ##G_{ab}## is a symmetric matrix, i.e. ##G_{ba} = G_{ab}##): $$S = \int dt \Big( \sum_{ab} G_{ab} \dot q^a\dot q^b-V(q)\Big)$$ Show (using Euler Lagrange's equation) that the following equation holds: $$\ddot q^d +...- JD_PM
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Please can I get some help finding the function of motion
Homework Statement:: find the function of motion Homework Equations:: none i could find the amplitude and the phase angle but i can't find the phase difference and the function of motion.- Alexan
- Thread
- Replies: 31
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Horizontal Circular Motion With Lagrange
In the situation described in the problem, the mass is moving on a horizontal circular path with constant velocity. Wouldn’t this make L and U both constant? Then the Lagrange equation would give 0 = 0, which isn’t what I’m looking for. Any help would be appreciated.- Fascheue
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

What is the minimum velocity needed?
I tried to solve this problem and this is what I could come through: When the object is moving, the force acting on object is the frictional force, so, it got to be μmg. So, F = ma and as F is μmg μmg = ma μg = a So, to find out the magnitude of the initial velocity v given to the smaller...- nineteen
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Relativistic motion of an electron in a uniform electric field
dv/dt is the acceleration, so I thought I could find the acceleration from F = qE = ma = dp/dt. But this is a relativistic case, so the proper acceleration is a = F/mγ3, where v in the gamma is the v of the electron and F = eE. However, I'm not sure if this is correct, because the constant τ...- Natchanon
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Do 4-divergences affect the eqs of motion for nth order perturbed fields?
Intuitively, I'd say that adding a 4-divergence to the Lagrangian should not affect the eqs of motion since the integral of that 4-divergence (of a vector that vanishes at ∞) can be rewritten as a surface term equal to zero, but... In some theories, the addition of a term that is equal to zero... -

Can a magnetic field ever cause a translation motion?
Lorentz Law says that for a charged particle moving with a velocity v in a magnetic field B then the force on it is given by $$ \mathbf{F} = q (\mathbf{v} \times \mathbf{B}) $$ Now, if I say that particle’s velocity and the magnetic field are aligned then according to Lorentz Law there will be...- Adesh
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
R
Projectile Motion : Work and Energy
The problem is based on a projectile-spring launcher. A ball is loaded into a tube that pushes back a spring and is then launched. The ball was launched straight horizontally not at an angle. I'm trying to find the work done on the ball by the spring. The info I have: Displacement of spring =...- ReCryptic
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Exercise about Constant Motion
NOTE: Sorry for my english. I use Google Translate! Comparing the performance with a friend of mine who is passionate about physics (and he is studying it by himself) we came to the same conclusion. In other words, we have calculated the time taken by both riders to reach the finish line. From...- jedimath
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Some quick questions concerning uniform acceleration and linear motion
Hello, I hope you are all having a great day ! I've got a physics test in a couple of days and I have some questions:1. In a calculation, if the acceleration is in m/s², I presume the speed also has to be in m/s and not in km/h ? 2. So with this graph (v with t), I have to find the total...- Ellio
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Clarifying Ambiguities in High School Physics Problems
I tried using the equation E(k)=1/2mv^2 and isolating for v but no mass was given. Then, I tried W=fd but there is no distance given. I don't know how to solve this.- physicslady123
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Energy Motion Motorcycle
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Z
I QM & Motion: Is There Consensus?
Is there consensus on the stance of QM in regards whether motion is actually continuous or not?- Zelebg
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Continuity Motion
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
A
Harmonic motion of four meter sticks
inertia of center = [(1/12) m*L^2 + m(L/2)^2]*4 inertia of center = (4m*L^2)/ 3 inertia around pin = (4m*L^2)/ 3 + 4m(L/ 2^(1/2) )^2 inertia around pin = (10m*L^2)/ 3 inertia around pin = (10*0.1*1^2)/ 3 = 0.33 kg*m^2 d= 1/2^(1/2) = 0.707m (m*g*d/inertia)^1/2 = 2pi/period...- ac7597
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help