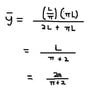unscientific
- 1,728
- 13
Homework Statement
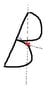
The question is attached in the first picture.
The Attempt at a Solution
The method they used makes perfect sense, but I can't see what's wrong with my method.
Their method
1. Find individual centre of mass of each semi-circle by Pappus's 2nd theorem
2. Sum up both moment contributions
3. Divide by total mass
My Method
Letting L = diameter of each semi-circle, and let d = distance from straight edge to centre of mass of entire frame.
First, we know the centre of mass must be half-way along the straight edge. Then, it must be perpendicularly above the straight edge.
Area of frame S = 2∏L2
By Pappus's 2nd theorem,
2∏L2 = (2∏d)(∏L)
d = L/∏
...
The only assumption I can think of here is that the straight edge has mass, which will affect the distance from the straight edge to centre of mass.
Thinking from the perspective of pappus's 2nd theorem, they assume that the only curve is the one above the y-axis. What happens if there's an additional curve y = 0?
In physical terms, the additional mass will definitely affect the height of c.g. above the y-axis. What happens if there is more than 1 curve? Is there still a way to describe the c.g. then?