- #1
ajack
- 6
- 0
In order to use BJT as a switch, it's very popular to do as the picture.
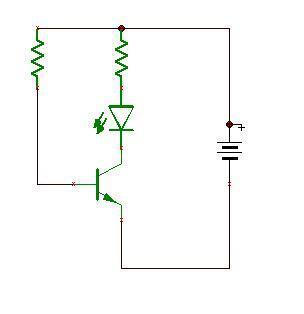
In the picture, V_B > V_E, so there's a current flow I_BE control the I_CE. In the other way, V_B > V_E generates the current I_CE, and the lamp will light on. But, I change the connection a little:
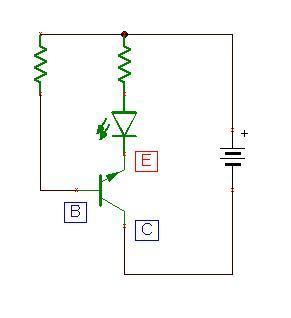
I'll let the V_B > V_C, it means, i change the position of C and E in that picture. And I found out that the lamp still light on. That means V_B > V_C also generates the current I_CE to make the light on. But in theory, only V_B > V_E make the light on
My questions are:
1. in saturated mode, there's no difference between C and E, you could use V_B > V_E or V_B > V_C and the lamp still light on, is it right?
2. Which way is better?
In the picture, V_B > V_E, so there's a current flow I_BE control the I_CE. In the other way, V_B > V_E generates the current I_CE, and the lamp will light on. But, I change the connection a little:
I'll let the V_B > V_C, it means, i change the position of C and E in that picture. And I found out that the lamp still light on. That means V_B > V_C also generates the current I_CE to make the light on. But in theory, only V_B > V_E make the light on
My questions are:
1. in saturated mode, there's no difference between C and E, you could use V_B > V_E or V_B > V_C and the lamp still light on, is it right?
2. Which way is better?