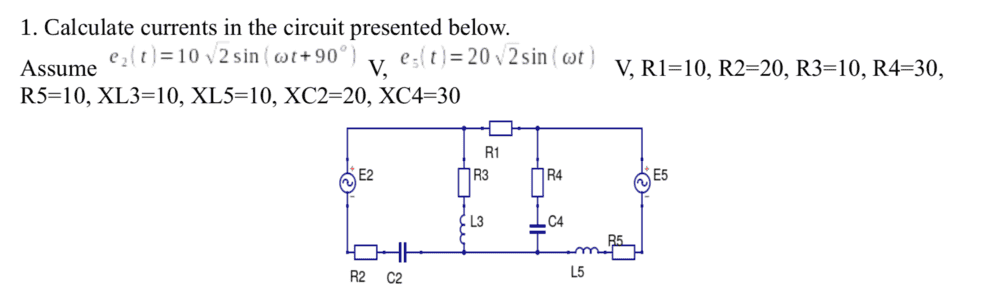
To convert from the time domain to the phasor domain in AC circuits, the voltages e2 and e5 can be expressed as e2 = j10 and e5 = 20, where "j" represents the imaginary unit. This conversion typically involves recognizing the peak values of sinusoidal signals and applying the RMS formula, which states that RMS voltage equals the peak voltage divided by the square root of 2. The discussion highlights the importance of understanding phasor representation and the relationship between time domain definitions and their corresponding phasor forms. Additionally, using Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) or Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) can help calculate branch currents in the circuit. Understanding these concepts is crucial for accurately analyzing AC circuits.