- #1
Xyius
- 508
- 4
Homework Statement
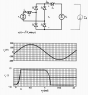
See The attached Images.
2. The attempt at a solution
The problem I am having with this is the following.
I do not know where he is getting these equations from. We haven't done anything like this in class. Although he keeps mentioning skills we learned in previous courses, which I took at another institution so it wasn't all exactly the same.
I see what looks like normalization constants from Fourier analysis? (2/pi) And square roots of 2 (usually indicates RMS). But I do not know the logic behind the equation. Also, why is he using "X" to indicate resistance? Is it a reactance? I also don't know where he gets the expression for the phase "u."
Sorry I know this might seem like a silly question but if anyone can help me out I would really appreciate it!