- #1
baldbrain
- 236
- 21
Homework Statement
I just have a problem with (A) & (B)
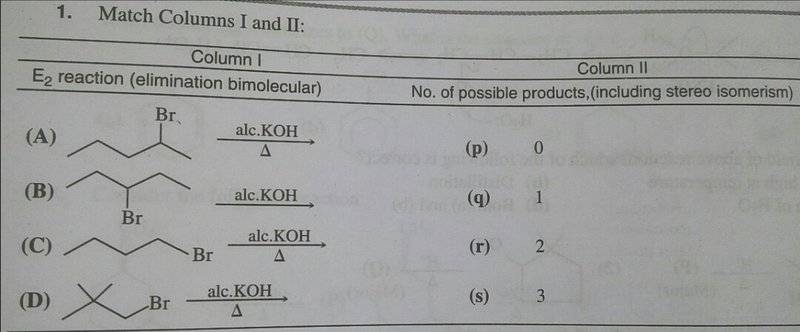
The attempt at a solution
Analysing all possible products;
(A) can give 1-pentene (minor) + 2-pentene (major). But you also have the E-Z diastereomers of 2-pentene. So that's total 3 possible products.
(B) will give only the diastereomers E & Z 2-pentene. So 2 possible products
Hence, (A)→(s) & (B)→(r)
But they've given (A)→(r) & (B)→(s)
How can it be?
I just have a problem with (A) & (B)
The attempt at a solution
Analysing all possible products;
(A) can give 1-pentene (minor) + 2-pentene (major). But you also have the E-Z diastereomers of 2-pentene. So that's total 3 possible products.
(B) will give only the diastereomers E & Z 2-pentene. So 2 possible products
Hence, (A)→(s) & (B)→(r)
But they've given (A)→(r) & (B)→(s)
How can it be?