bbuilder
- 14
- 0
Homework Statement
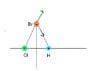
A hydrogen chloride molecule (HCl) has a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the chlorine atom. The HCl molecule is placed at
A.
There will be force on the bromide ion in the +x direction.
B.
There will be force on the bromide ion in the -x direction.
C.
There will be force on the bromide ion in the +y
There will be no force on the bromide ion. The attractive force from the positively charged hydrogen will be canceled out by the repulsive force of the negatively charged chlorine.
Homework Equations
p=qd
The Attempt at a Solution
I might be overthinking this problem. I was thinking that the bromide ion be in the positive x-direction to attract it to the partial positive negative ion. I'm confused about how the y-direction might come into play in this problem. I was also thinking that these charges might cancel out because they are directly opposite of each other on the x-axis.
Last edited: