asifrulzz
- 4
- 0
equivalent resistance of tricky circuits?
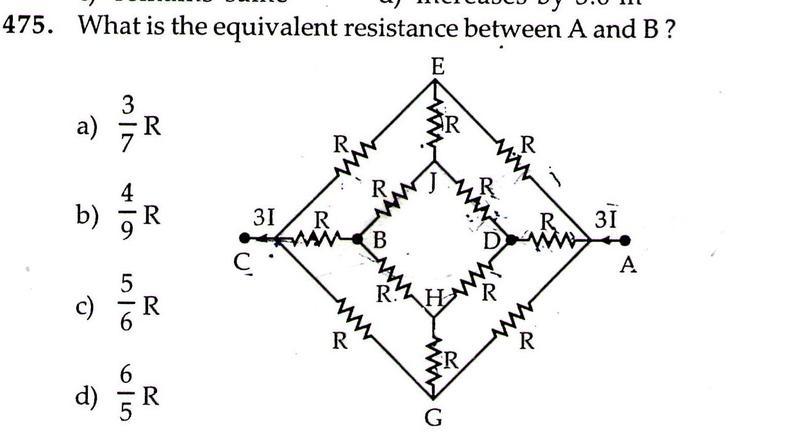
what is the equivalent resistance between A and B?
kirchoffs law for voltage and current
i got the equivalent resistance between A to C as 3R/4
but i have to find the resistance between A to B but point B is in the middle of the circuit and i don't know how to approach it
i am stuck on this
please help!
Homework Statement
what is the equivalent resistance between A and B?
Homework Equations
kirchoffs law for voltage and current
The Attempt at a Solution
i got the equivalent resistance between A to C as 3R/4
but i have to find the resistance between A to B but point B is in the middle of the circuit and i don't know how to approach it
i am stuck on this
please help!
Last edited: