Discussion Overview
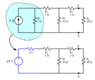
The discussion revolves around finding the Thevenin equivalent circuit external to a load resistor (RL) in a given electrical circuit. Participants engage in calculations related to resistances, voltages, and currents, while exploring the differences between Thevenin and Norton equivalents. The scope includes theoretical calculations and practical applications of circuit analysis.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant calculates the Thevenin resistance (Rth) as 7Ω and attempts to find the Thevenin voltage (Vth) based on circuit configurations.
- Another participant questions the identification of a 2Ω resistor in the circuit, indicating a lack of clarity in the initial post.
- Some participants provide simulation results, indicating a Thevenin current of 1.786A, but express confusion about current values in series and parallel configurations.
- There is a discussion about the differences between Thevenin and Norton equivalents, with some participants noting that textbooks may mix the two concepts.
- Several participants attempt to clarify the steps for calculating the Thevenin equivalent, emphasizing the need to find the open circuit voltage (VAB) when RL is removed.
- One participant calculates V3 as 25V and Isc as 175A, but another challenges the correctness of these calculations based on circuit configurations.
- There are multiple calculations presented for voltages across different resistors, with participants attempting to reconcile their results with the expected values.
- Confusion arises regarding the voltage across R2 and the relationship to Vth, with participants debating the correct approach to find these values.
- One participant expresses uncertainty about the origin of a specific current value (2.173), indicating a need for clarification on its calculation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the calculations and interpretations of the Thevenin equivalent. There are competing views on the correct approach to finding the Thevenin voltage and resistance, as well as confusion regarding the definitions and applications of Thevenin and Norton theorems.
Contextual Notes
Some calculations depend on assumptions about circuit configurations, and there are unresolved mathematical steps regarding the relationships between different resistors and currents. The discussion reflects varying levels of understanding and interpretations of circuit analysis principles.