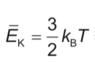Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around the application of the ideal gas law in the context of a cylinder filled with gas. Participants are exploring the relationship between pressure, force, and the number of gas molecules, particularly in relation to the equations governing gas behavior.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- The original poster attempts to apply the ideal gas law but encounters confusion regarding the incorporation of Boltzmann's constant and the transition from pressure to force. Some participants question how to relate pressure to kinetic energy and clarify the distinction between the number of moles and the number of molecules in the context of the gas law.
Discussion Status
Participants are actively engaging with the problem, offering insights into the necessary conversions between pressure and force, as well as the implications of using different quantities (moles vs. molecules). There is a recognition of the need to clarify these concepts, and some guidance has been provided regarding the equations involved.
Contextual Notes
There is a noted confusion regarding the use of Boltzmann's constant in conjunction with the ideal gas law, as well as the distinction between the number of moles and the number of molecules, which may affect the approach to the problem.