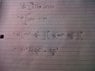azserendipity said:
The formulas I got the formulas for an and bn from my lecture notes. The exact formulas are written as:
Periodic functions as Fourier series
f(x)= \frac{1}{2}a{0}+Ʃ^{∞}_{n=1}{an cosnx + bn sinnx=\frac{a0}{2} + a1 cosx + a2 cos2x+...+b1 sinx + b2 sin2x +...
The above formula is applicable to functions with a period of ##2\pi##.
a0=\frac{2}{T}\int^{T/2}_{-T/2} f(x)dx ie. 2xmean value of f(x) over period
an= \frac{2}{T}\int^{T/2}_{-T/2} f(x) * cosnx dx ie. 2x mean value of f(x)*cosnx over period
bn= \frac{2}{T}\int^{T/2}_{-T/2} f(x) * sinnx dx ie. 2x mean value of f(x)*cosnx over period
These formulas aren't quite right. It's mixing up the case where the period is ##2\pi## and the more general case of a period of T.
When the period is ##2\pi##, you have
\begin{align*}
f(x) &= \frac{a_0}{2} + \sum_{n=1}^\infty (a_n \cos nx + b_n \sin nx) \\
a_n &= \frac{1}{\pi}\int_{-\pi}^\pi f(x)\cos nx\,dx \\
b_n &= \frac{1}{\pi}\int_{-\pi}^\pi f(x)\sin nx\,dx
\end{align*}
When the period is T, you have
\begin{align*}
f(x) &= \frac{a_0}{2} + \sum_{n=1}^\infty (a_n \cos n\omega_0x + b_n \sin n\omega_0x) \\
a_n &= \frac{2}{T}\int_{-T/2}^{T/2} f(x)\cos n\omega_0x\,dx \\
b_n &= \frac{2}{T}\int_{-T/2}^{T/2} f(x)\sin n\omega_0x\,dx
\end{align*}where ##\omega_0 = 2\pi/T##. If you set ##T=2\pi## in these formulas, you'll recover the ones above.
For your particular f(x), the period is ##2\pi##, so you can use the first set of formulas.