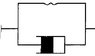
How Does Adding a Damper Affect the Stiffness of Springs in Parallel?
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
Adding a damper in parallel with springs affects the overall stiffness and impedance of the system. The total stiffness for springs in parallel is calculated using the formula 1/k(total) = 1/k1 + 1/k2, while the total impedance in the Laplace domain is represented as k + sc, where k is the spring coefficient and c is the damper coefficient. This configuration is relevant in the study of damped harmonic oscillators, which can be further explored in the provided Wikipedia link.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of spring mechanics and stiffness calculations
- Familiarity with damping concepts in mechanical systems
- Knowledge of Laplace transforms and their application in system analysis
- Basic principles of harmonic oscillators
- Study the principles of damped harmonic oscillators in detail
- Learn about the application of Laplace transforms in mechanical systems
- Explore the effects of different damping coefficients on system behavior
- Investigate real-world applications of springs and dampers in engineering
Mechanical engineers, physics students, and anyone interested in the dynamics of spring-damper systems and their applications in real-world scenarios.
Similar threads
- · Replies 15 ·
- · Replies 11 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
Graduate
Motion of a spring that has mass
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 2 ·