Meteo
- 12
- 0
0.250 mol of a monatomic gas follows the process shown in the figure.
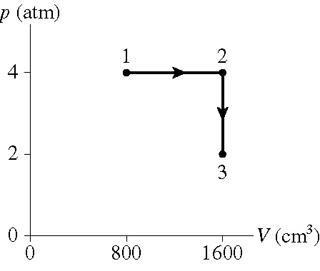
How much heat energy is transferred to or from the gas during process 1 to 2?
How much heat energy is transferred to or from the gas during process 2 to 3?
What is the total change in thermal energy of the gas?
I am not sure how to relate pressure and volume to heat energy.
I have pV=nRT and \Delta E_{th}=W+Q
Also for the third question. would I just subtract the energy at point 3 from the energy at
point 1?
How much heat energy is transferred to or from the gas during process 1 to 2?
How much heat energy is transferred to or from the gas during process 2 to 3?
What is the total change in thermal energy of the gas?
I am not sure how to relate pressure and volume to heat energy.
I have pV=nRT and \Delta E_{th}=W+Q
Also for the third question. would I just subtract the energy at point 3 from the energy at
point 1?
Attachments
Last edited: