- #1
LovePhys
- 57
- 0
Hello everyone,
A friend of mine came up with this question in class and I really do not have a good answer.
Suppose you have a convex lens that has been cut in half horizontally and the top half removed.
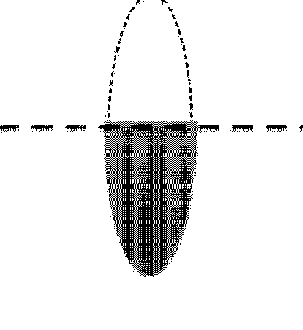
The question is: Will the bottom half of the lens still form an image?
I really have no idea of how approach this problem. Normally, suppose that an object is placed on the principal axis, then one of the three special rays is supposed to go through the optical center of the lens. But in this case, the top half has been removed, would that have an impact on the optical center?
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thank you,
LovePhys
A friend of mine came up with this question in class and I really do not have a good answer.
Suppose you have a convex lens that has been cut in half horizontally and the top half removed.
The question is: Will the bottom half of the lens still form an image?
I really have no idea of how approach this problem. Normally, suppose that an object is placed on the principal axis, then one of the three special rays is supposed to go through the optical center of the lens. But in this case, the top half has been removed, would that have an impact on the optical center?
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thank you,
LovePhys