- #1
jofree87
- 38
- 0
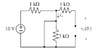
What is the voltage across vc(0) in the diagram below?
The solution says its 10V but I don't know how they got that.
Through KVL, I got 0V.
Since all the current flows through the left most circuit, iA = 10/1000 = .01A
3k and 1k(right) resistors have no current.
-10 + 1000iA + vc = 0
vc = 0?
Am I doing something wrong here?
Edit: After applying nodal analysis, I got 10V, so I must be applying KVL wrong then?
The solution says its 10V but I don't know how they got that.
Through KVL, I got 0V.
Since all the current flows through the left most circuit, iA = 10/1000 = .01A
3k and 1k(right) resistors have no current.
-10 + 1000iA + vc = 0
vc = 0?
Am I doing something wrong here?
Edit: After applying nodal analysis, I got 10V, so I must be applying KVL wrong then?
Attachments
Last edited: