nik2011
- 11
- 0
Hello,
Given a simple electric circuit like the one below (taken from Wikipedia)
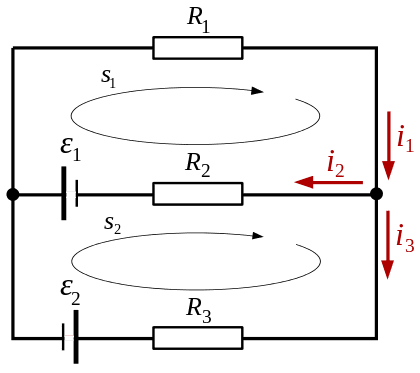
If we were to start from tracking all the forces acting on each individual free electron in the circuit, would it be possible to eventually find all the currents and voltages acting in the circuit?
Probably a computer program would be designed to perform the modelling.
Anyway, tracking each individual free electron is obviously highly impractical and likely the existing computers are not powerful enough.
But the real question is if all the essential facts and laws necessary to make such a simulation possible in principle are known to physics? And if so, what are these laws?
In case tracking individual free electrons is absolutely infeasible even in principle: What is the deepest level of details describing the phenomena/processes happening in an electrical circuit that is known to the contemporary physics?
A note that hopefully helps clarify the question:
Please contrast the simulation described in this question with an approach used in software based on SPICE: applications based on SPICE derive a system of linear equations from the modeled circuit and solve it. This SPICE-based or similar kind of simulators is not what the question is about.
Thank you!
Given a simple electric circuit like the one below (taken from Wikipedia)
If we were to start from tracking all the forces acting on each individual free electron in the circuit, would it be possible to eventually find all the currents and voltages acting in the circuit?
Probably a computer program would be designed to perform the modelling.
Anyway, tracking each individual free electron is obviously highly impractical and likely the existing computers are not powerful enough.
But the real question is if all the essential facts and laws necessary to make such a simulation possible in principle are known to physics? And if so, what are these laws?
In case tracking individual free electrons is absolutely infeasible even in principle: What is the deepest level of details describing the phenomena/processes happening in an electrical circuit that is known to the contemporary physics?
A note that hopefully helps clarify the question:
Please contrast the simulation described in this question with an approach used in software based on SPICE: applications based on SPICE derive a system of linear equations from the modeled circuit and solve it. This SPICE-based or similar kind of simulators is not what the question is about.
Thank you!