- #1
allora_97
- 13
- 0
Newton's forces on a box!
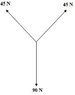
Two 45 N forces and a 90 N force act on a hanging box as shown in the picture below.
Will the box experience acceleration?
1. Yes; upward.
2. No; it is balanced.
3. Unable to determine without the angle.
4. Yes; downward.
F= ma
Will the two forces at the top result in a +y direction force of 45 or 90, or is it something else.
Homework Statement
Two 45 N forces and a 90 N force act on a hanging box as shown in the picture below.
Will the box experience acceleration?
1. Yes; upward.
2. No; it is balanced.
3. Unable to determine without the angle.
4. Yes; downward.
Homework Equations
F= ma
The Attempt at a Solution
Will the two forces at the top result in a +y direction force of 45 or 90, or is it something else.