- #1
DanielSauza
- 8
- 0
I was reading a bit about comrpessible flow and I came upon a problem, there's a diffuser which has air at Ma=0.9 at its inlet and the air comes out at 0.65, how should I go about finding the ratio of the inlet and outlet areas?
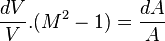
I know It's related to this equation but I'm unsure about how to use it (Should I turn Ma^2 into V terms or should I just use the Ma number at the outlet?)
I know It's related to this equation but I'm unsure about how to use it (Should I turn Ma^2 into V terms or should I just use the Ma number at the outlet?)