clalburn1420
- 12
- 0
Hi All,
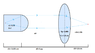
I need help determining focal length value in a two lens system. In the set up, the light source (object) is within a tube, a medium surrounds it with refractive index n1=1.52. The end of the tube is met with a curved convergent surface, the center of which is 0.635 cm away and focal length Fχ. The light passes through the surface into air, and then travels a distance of 3 cm to another thin lens (biconvex) with a focal length of 1.8 cm and refractive index n2=1.406. The light then travels through a medium of refractive index n3=1.336 to focus the image at 1.8 cm from the lens. (look to attached image).
How do I determine the focal length (Fx) of the first lens?
What would happen if the first lens was divergent? Would it still form the image?
What would happen in the size of the second lens changed shape?
I know how to solve for a two lens system using the thin lens equation but its really stumping me having the light source inside of the lens medium.
Any help would be so appreciated.
I need help determining focal length value in a two lens system. In the set up, the light source (object) is within a tube, a medium surrounds it with refractive index n1=1.52. The end of the tube is met with a curved convergent surface, the center of which is 0.635 cm away and focal length Fχ. The light passes through the surface into air, and then travels a distance of 3 cm to another thin lens (biconvex) with a focal length of 1.8 cm and refractive index n2=1.406. The light then travels through a medium of refractive index n3=1.336 to focus the image at 1.8 cm from the lens. (look to attached image).
How do I determine the focal length (Fx) of the first lens?
What would happen if the first lens was divergent? Would it still form the image?
What would happen in the size of the second lens changed shape?
I know how to solve for a two lens system using the thin lens equation but its really stumping me having the light source inside of the lens medium.
Any help would be so appreciated.