- #1
lehnim
- 4
- 0
Given this setup
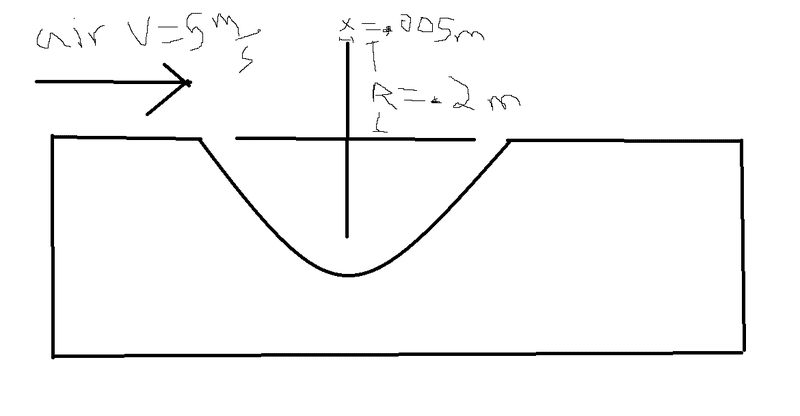
note: i just created arbitrary values if it helps, if not working with variables to find a general solution works fine too
I am trying to find what the optimal width(would look like depth in the photo) of the wheel would be to generate the most power. I am stumped on how to begin the problem and am looking for ideas.
Thanks in advance
note: i just created arbitrary values if it helps, if not working with variables to find a general solution works fine too
I am trying to find what the optimal width(would look like depth in the photo) of the wheel would be to generate the most power. I am stumped on how to begin the problem and am looking for ideas.
Thanks in advance
Last edited by a moderator: