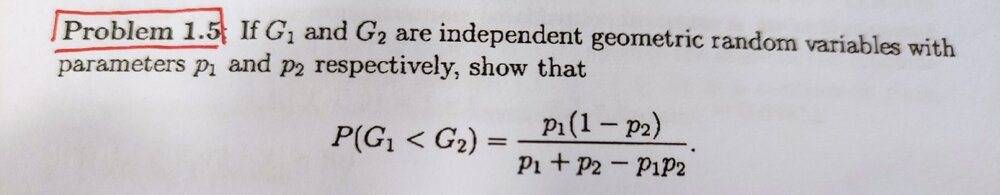SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the proof of a formula involving two geometric random variables, specifically addressing the error in the initial equation presented. The key correction involves summing the cases where G1 = k instead of G1 ≤ k, which leads to multiple counting of cases. This clarification is essential for accurately deriving the probability distribution associated with the geometric random variables.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of geometric random variables
- Familiarity with probability theory
- Knowledge of summation notation and its implications
- Basic skills in mathematical proofs
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of geometric random variables
- Learn about probability distributions and their applications
- Explore techniques for avoiding multiple counting in combinatorial proofs
- Investigate advanced topics in probability theory, such as conditional probability
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, statisticians, and students studying probability theory, particularly those interested in random variables and their properties.