- #1
physics222
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
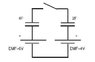
At t=0m the switch is open and both capacitors are uncharged. What are the charges on each plate (magnitude and sign) of each capacitor long after the switch is closed and capacitors are fully charged?
Homework Equations
q=C E(1-e^(-t/RC)
The Attempt at a Solution
I was sick during the weed we did circuits and am pretty lost. I get confused about what is happening conceptually and how to use that to find an answer.