- #1
drawar
- 132
- 0
Homework Statement
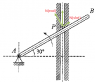
Particle P has a mass of 1kg and is confined to move along the smooth vertical slot due to the rotation of the arm Ab. Assume that at the instant as shown, the acceleration of the particle P is 2.46 m/s^2 upward. Determine the normal force N(rod) on the particle by the rod and the normal force N(slot) on the particle by the slot in the position shown. Frictions forces are negligible.
----N(rod) ---- N(slot)
A. 14.2 N ---- 7.1 N
B. 10.5 N ---- 3.6 N
C. 7.1 N ---- 14.2 N
D. 3.2 N ---- 1.6 N
Homework Equations
F= maThe Attempt at a Solution
F = ma = 2.46 N
The force acting on the particle can be resolved into 2 components
N(rod) = F x cos(30) = 2.13 N
N(slot) = F x sin(30) = 1.23 N
The answer does not match any of the choices provided. Can someone help me figure out what I'm doing wrong? Thanks
Last edited: