keximaze
- 7
- 0
1. Three guy wires hold a pole BO as shown. The resultant R of the forces due to the three wires has a magnitude of 1000-N and is directed on the pole BO. Force F2 and F3 have a magnitude of 400-N and 500-N, respectively. The distance from point A to point D is 5-m. Find the tension in cable BD.
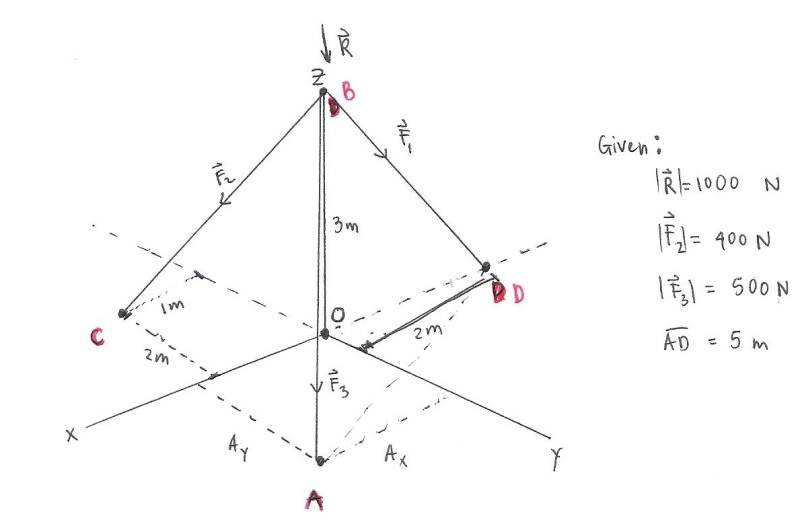
Summation of all the forces = 0
F1 + F2 + F3 + R = 0
F = F*(unit vector)
On the solution below, I first established vectors F2 and F3 using the equation F=F*(unit vector). After that, I obtained a relation between Ax and Ay using the length AD.
I ended up with a set of 4 equations and 3 unknowns (the circled part below). I could get an answer but I am not sure if its right. Also, I believe that this is not the most practical way of solving the problem.
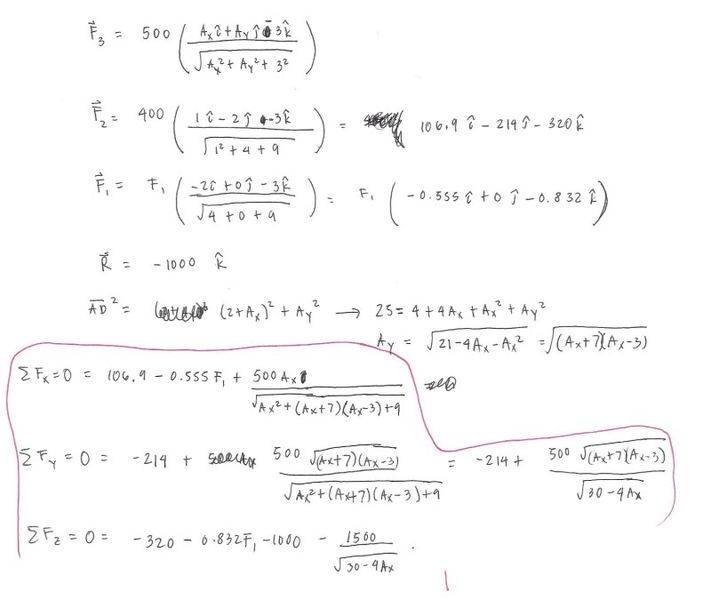 Could anyone please help me find a better way of solving this problem? Thanks in advance.
Could anyone please help me find a better way of solving this problem? Thanks in advance.
Homework Equations
Summation of all the forces = 0
F1 + F2 + F3 + R = 0
F = F*(unit vector)
The Attempt at a Solution
On the solution below, I first established vectors F2 and F3 using the equation F=F*(unit vector). After that, I obtained a relation between Ax and Ay using the length AD.
I ended up with a set of 4 equations and 3 unknowns (the circled part below). I could get an answer but I am not sure if its right. Also, I believe that this is not the most practical way of solving the problem.