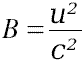Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around demonstrating the Lorentz invariance of the Euler-Lagrange equations, particularly in the context of Einstein's extended energy concept. Participants explore theoretical aspects, seek clarification on related concepts, and share resources.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- One participant requests assistance in showing that the Euler-Lagrange equations are Lorentz invariant, specifically when using Einstein's extended energy concept.
- Another participant suggests consulting a book by Greiner on relativistic quantum mechanics for more information.
- A participant asserts that the Euler-Lagrange equations are derived covariantly from an invariant action integral, indicating their covariance with respect to the Lorentz group.
- A participant expresses uncertainty about the relationship between Einstein's extended energy concept and the Euler-Lagrange equations, seeking clarification.
- One participant shares their background, indicating a lack of familiarity with covariances, tensors, and group theory, and mentions the context of their inquiry as part of a philosophical paper.
- A participant notes their difficulty in understanding how Lorentz transformations apply in generalized coordinates, having only worked with Cartesian coordinates.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of understanding and familiarity with the concepts discussed. There is no consensus on how to demonstrate the Lorentz invariance of the Euler-Lagrange equations, and multiple viewpoints and uncertainties remain present.
Contextual Notes
Participants mention limitations in their understanding of advanced topics such as covariances, tensors, and group theory, which may affect their ability to engage with the discussion fully. There are also unresolved questions regarding the application of Lorentz transformations in generalized coordinates.