Bolter
- 262
- 31
- Homework Statement
- See image attached below
- Relevant Equations
- v = k * sqrt(T)
Here is the Q

Very unsure about how to approach this question but this is what I have tried
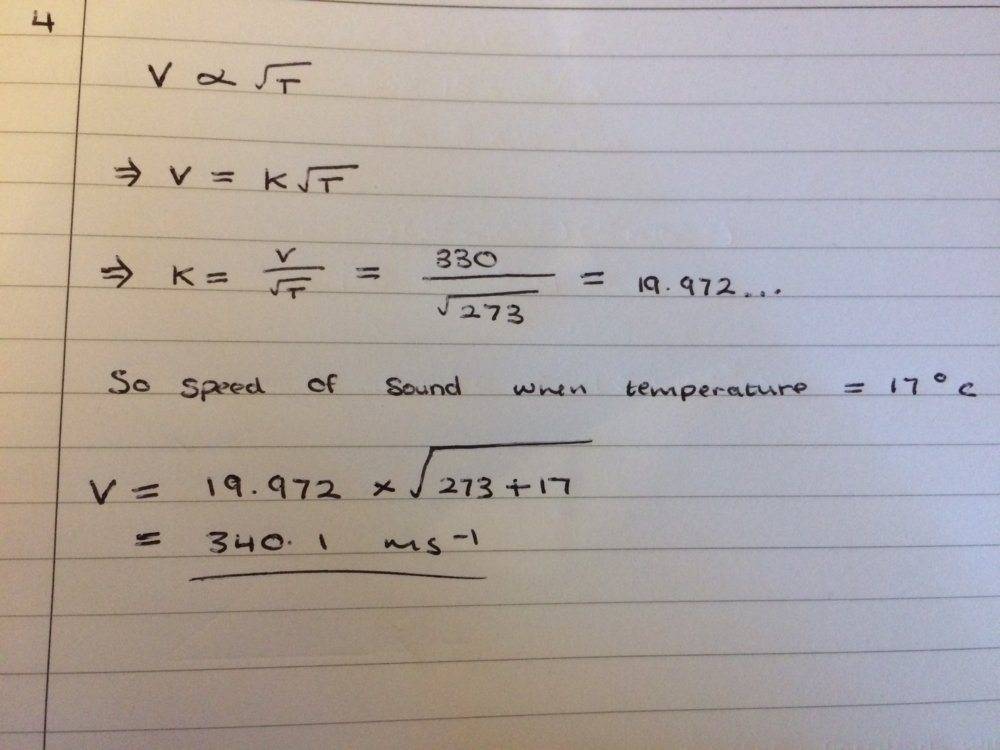
Any help would be really appreciated! Thanks
Very unsure about how to approach this question but this is what I have tried
Any help would be really appreciated! Thanks