DrVirz
- 24
- 0
Hi all,
Just doing some thermo study and am stuck on a question. I am not sure where to start this Q as normally I am given a property at the exit..?
Any help is appreciated.
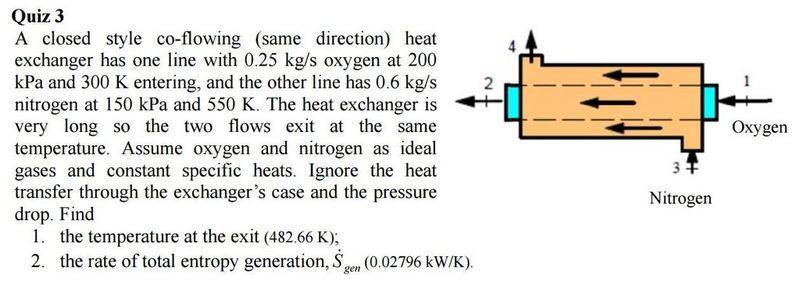
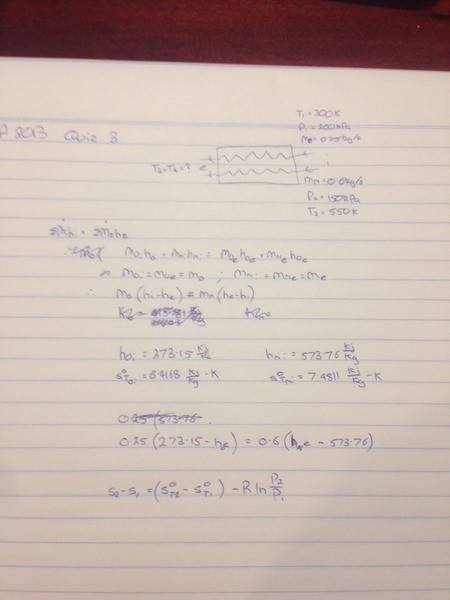
Just doing some thermo study and am stuck on a question. I am not sure where to start this Q as normally I am given a property at the exit..?
Any help is appreciated.