- #1
gnits
- 137
- 46
- Homework Statement
- To calculate torque on a supported beam
- Relevant Equations
- equate forces and torques
Could I please ask for help with the last part of the following question?

I have the first two parts done, answers are:
Distance of COG from A = a(1+n)/n
and W1 = W(1+n)/3
I can't see how to go about the last part. Here's my diagram for the system prior to the torque L being added:
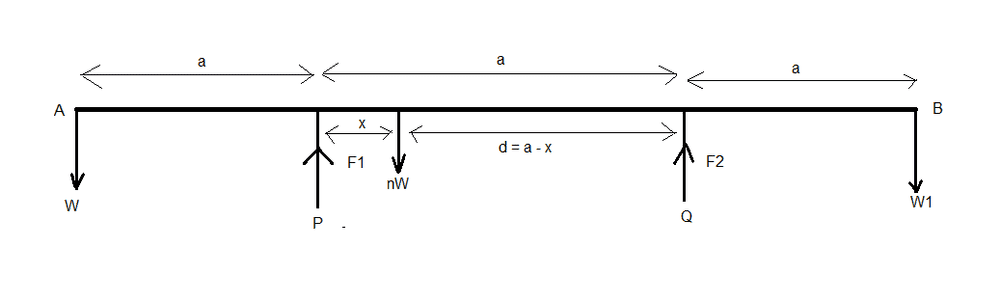
In this situation we have (are told) F1 = F2 = F say, and so W1 + W + nW = 2F and so as we know W1 in terms of W and n we have F = 2W(n+1)/3 and we are told that after torque L is applied then this increases by 1.5 times, so now F1 = W(n+1) and so F2 = W(n+1)/3. As F1 has increased then we know that L is counter-clockwise.
Can't see though what equation to set up to calculate the L which would lead to this value for F1.
Thanks for any help,
Mitch.
I have the first two parts done, answers are:
Distance of COG from A = a(1+n)/n
and W1 = W(1+n)/3
I can't see how to go about the last part. Here's my diagram for the system prior to the torque L being added:
In this situation we have (are told) F1 = F2 = F say, and so W1 + W + nW = 2F and so as we know W1 in terms of W and n we have F = 2W(n+1)/3 and we are told that after torque L is applied then this increases by 1.5 times, so now F1 = W(n+1) and so F2 = W(n+1)/3. As F1 has increased then we know that L is counter-clockwise.
Can't see though what equation to set up to calculate the L which would lead to this value for F1.
Thanks for any help,
Mitch.