RoyalFlush100
- 56
- 2
Homework Statement
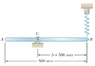
The uniform rod shown has mass 6 kg and is attached to a spring of constant k = 820 N/m. End B of the rod is depressed 10 mm and released.
Determine the period of vibration.
Picture is attached below
Homework Equations
Fs = kx
W = mg
The Attempt at a Solution
I honestly don't quite know how to even start a problem like this.
Fs = (820 N/m)(0.010 m) = 8.2 N
W = (6 kg)(9.81 N/kg) = 58.86 N
The spring force will act on the right end of the bar and the weight will act in the middle (@400 mm).
How am I supposed to proceed on this type of question? Do I need the torque about C?