- #1
saad87
- 85
- 0
I have the following circuit wired up on a protoboard.
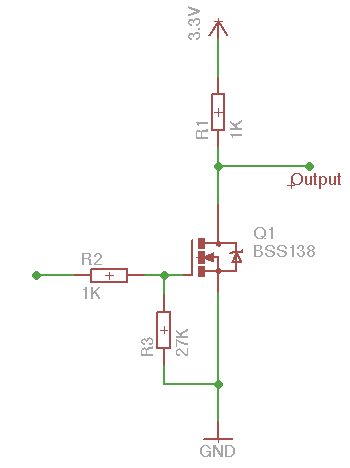
The datasheet for the BSS138 MOSFET is here. I'm puzzled regarding what I'm seeing happen with this circuit - when I apply 3.3V at the gate resistor, the MOSFET turns on fully and I see 3mV at the output. This, of course, is expected.
However, if I remove 3.3V from the gate resistor, the pull-down resistor turns the gate off. I expected to see approximately 3.3V at the output, yet I only see 2.7V. If I replace the 3.3V on R1 with 5V, the output shows 4V. In other words, a volt is being dropped on R1 when the MOSFET is off. Is this expected? Somehow, I expected the MOSFET to have an immensely high resistance when off and hence expected approximately 5V being dropped on it when it's off.
Are my expectations wrong for this MOSFET?
The datasheet for the BSS138 MOSFET is here. I'm puzzled regarding what I'm seeing happen with this circuit - when I apply 3.3V at the gate resistor, the MOSFET turns on fully and I see 3mV at the output. This, of course, is expected.
However, if I remove 3.3V from the gate resistor, the pull-down resistor turns the gate off. I expected to see approximately 3.3V at the output, yet I only see 2.7V. If I replace the 3.3V on R1 with 5V, the output shows 4V. In other words, a volt is being dropped on R1 when the MOSFET is off. Is this expected? Somehow, I expected the MOSFET to have an immensely high resistance when off and hence expected approximately 5V being dropped on it when it's off.
Are my expectations wrong for this MOSFET?