- #1
Thadis
- 44
- 0
Ended up figuring out how to solve this problem. I just was not expecting certain parts of the results which lead me to believe I did it wrong.
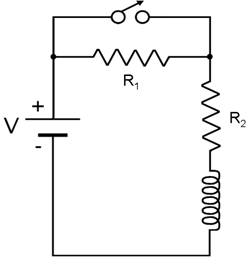
Voltage of battery is 5V
Resistors are 5 Ohms
The solenoid has no internal resistance
1.Need to find V_2 before switch is opened
2.The current through the solenoid right after the switch has been opened.
3. The current through R_2 and R_1 right after the switch has been opened.
4. Voltage across R_1 right after the switch has been opened.
5. Voltage across R_1 if it was 5 Mohms right after the switch has been opened.
V=IR
Kirchhoff's Loop Rule
That a solenoid will want to resist any change in current.
1. The voltage across R_2 will be 5V because the loop that consists of the switch and resistor has to have a voltage drop of 5 V and the resistor is the only element with a voltage drop on that loop.
2. The current through the solenoid right after the switch is open will be 1 A as the solenoid will want to keep the same current as before.
3. 1 A as the current will be same as the solenoid.
4. The voltage drop across both of the resistors will be 5 V. The solenoid will add additional voltage to create the greater voltage.
5. 5*10^6 V as the current will still be 1 A.I know I probably have flawed logic in here somewhere though I just do not know exactly how a solenoid will effect this circuit after the switch is thrown.
Homework Statement
Voltage of battery is 5V
Resistors are 5 Ohms
The solenoid has no internal resistance
1.Need to find V_2 before switch is opened
2.The current through the solenoid right after the switch has been opened.
3. The current through R_2 and R_1 right after the switch has been opened.
4. Voltage across R_1 right after the switch has been opened.
5. Voltage across R_1 if it was 5 Mohms right after the switch has been opened.
Homework Equations
V=IR
Kirchhoff's Loop Rule
That a solenoid will want to resist any change in current.
The Attempt at a Solution
1. The voltage across R_2 will be 5V because the loop that consists of the switch and resistor has to have a voltage drop of 5 V and the resistor is the only element with a voltage drop on that loop.
2. The current through the solenoid right after the switch is open will be 1 A as the solenoid will want to keep the same current as before.
3. 1 A as the current will be same as the solenoid.
4. The voltage drop across both of the resistors will be 5 V. The solenoid will add additional voltage to create the greater voltage.
5. 5*10^6 V as the current will still be 1 A.I know I probably have flawed logic in here somewhere though I just do not know exactly how a solenoid will effect this circuit after the switch is thrown.
Last edited: