Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the electric field intensity due to a point charge, line charge, and plane charge. Participants are sharing their attempts and seeking confirmation on their calculations.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related, Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant presents an equation for E2, suggesting it is E2=2*10^-9*(1/√2ŷ+1/√2ž)/(2πεo√2), and asks for confirmation of their answer.
- Another participant agrees with the equation for E2 and states that everything else is correct, implying a level of confidence in the calculations presented.
- A later reply clarifies that d^ is a unit vector, confirming a detail related to the notation used in the equations.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the correctness of the equation for E2, but there is no consensus on the overall correctness of the entire solution as only one participant has explicitly confirmed their calculations.
Contextual Notes
There may be limitations related to the assumptions made in the calculations, such as the specific conditions under which the electric field is being evaluated, but these are not fully explored in the discussion.
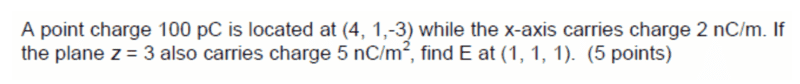

 Could someone please confirm my answer?
Could someone please confirm my answer?