Discussion Overview
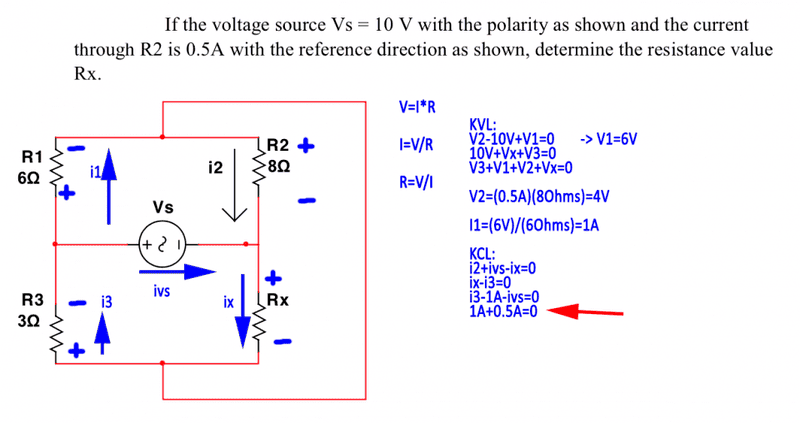
The discussion revolves around solving a circuit problem using Ohm's Law, specifically focusing on the effects of adding a wire to the circuit and how it influences current and voltage calculations. Participants explore various approaches to analyze the circuit, including inspection and redrawing the circuit layout.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about current values not summing to zero and questions the impact of the added wire on the circuit.
- Another participant notes that the current Ix - I3 is not necessarily zero due to the wire, suggesting that the voltage on the shorting wire can be determined from known values.
- There is a suggestion that a simpler solution may be possible through inspection rather than extensive calculations.
- Participants discuss the voltage drop across an 8Ω resistor and its implications for the potential of the wire, with one asserting that the wire's potential is 4V if ground is assumed at the negative terminal of the source.
- Concerns are raised about whether previous calculations are incorrect due to not accounting for the wire's properties, with an explanation that the wire is an ideal conductor with uniform potential.
- One participant is advised to redraw the circuit to clarify the relationships between components and potentials, with specific instructions on how to orient the voltage source.
- There is a confirmation that once the ground is fixed, known potentials can help find currents in the resistors.
- A participant proposes combining resistances of R1 and R3 to find an equivalent resistance, which is affirmed by another participant.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express uncertainty about the implications of the wire on their calculations, and while some points receive agreement, there is no overall consensus on the correct approach or final solution to the problem.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include potential misunderstandings about circuit grounding, the properties of wires in circuits, and the assumptions made regarding voltage and current distribution.