- #1
Karol
- 1,380
- 22
Homework Statement
A test was made with a basket and 20 gram weights. they were put in the basket which hang on a spring, the basket was raised and released. the period was measured for a few number of weights in the basket. the results are as follows. the first of every pair is the number of weights and the second is the period in seconds:
(2, 0.53), (3, 0.60), (4, 0.66), (5, 0.72), (6, 0.77)
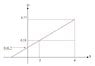
Draw a graph of T2 as a function of the number of weights, n. comes out a straight line.
What is the spring constant and the weight of the basket.
Homework Equations
Period: $$T=2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{c}}$$
The Attempt at a Solution
From the above equation $$T^2=\frac{4\pi^2}{c}\cdot m$$
The slope $$\frac{4\pi^2}{c}$$ based on the last and first couples:
##\frac{4\pi^2}{c}=\frac{0.77-0.53}{(6-2)\cdot 0.02}=3\rightarrow c=13.2##
The spring constant c should be around 10[N/m]
The intersection with the T2 axis: i take the first pair:
##0.53=3\cdot 0.04+B\rightarrow B=0.41##
I insert this B into: $$T^2=\frac{4\pi^2}{c}\cdot m$$
And get:
##0.41=3\cdot m_{basket} \rightarrow m_{basket}=0.14##
It should be around 30 grams
Attachments
Last edited: