Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating components of an AC voltage waveform, specifically involving harmonics and their contributions to the overall waveform. Participants explore the mathematical expressions for the waveform, sketching the harmonic components, and determining instantaneous voltage and percentage error at a specific time. The scope includes theoretical calculations and homework-related queries.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Participants discuss the expression for the voltage waveform, with one participant proposing a formula that includes the fundamental and harmonic components.
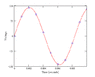
- There is a suggestion to plot the waveforms of the 3rd and 5th harmonics, with varying opinions on the appropriate time period for the sketch.
- Some participants express uncertainty about the phase angle for the 3rd harmonic and its implications on calculations.
- Calculations for the instantaneous voltage at 20ms are presented, with participants verifying each other's results and discussing the correctness of their approaches.
- There is a debate regarding the calculation of percentage error, with differing opinions on whether to use RMS or instantaneous values for comparison.
- One participant emphasizes the importance of using the correct denominator when calculating percentage error, leading to a refinement of the error calculation method.
- Participants question the necessity of converting to peak values and discuss the implications of using RMS values in their calculations.
- There are multiple attempts to clarify the calculations for the actual and ideal waveforms at 20ms, with some participants expressing confusion over their results.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the need to calculate the waveform components and the importance of accuracy in their calculations. However, there are multiple competing views regarding the correct approach to calculating percentage error and the use of RMS versus instantaneous values, indicating that the discussion remains unresolved.
Contextual Notes
Some calculations depend on assumptions about phase angles and whether to convert to peak values. There are unresolved mathematical steps regarding the correct method for calculating percentage error, and participants express uncertainty about the time intervals used for plotting waveforms.