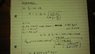darksupernova
- 2
- 0
Hey guys,
Ive got a little stuck calculating the mass flow rate of a choked flow through a de laval nozzle.
I have been given a formula to use for theoretical max and experimental but they seem to be SO far apart, I am sure I am missing something.
Given data:
Density of water 1000 kg/m^3
Throat diameter (nozzle) 4.79mm
Exit diameter (nozzle) 5.54mm
Probe diameter 3.30mm
Coefficient of discharge of orifice plate 0.6
orifice diameter 27.03mm
pipe diameter 76.2mm
gamma ratio of specific heats 1.4
gas constant 287 J/(kg K)
Absolute zero 273 degrees c / 0 K
Delta H = 2" = 0.0508m
See useful equations in attached image.
The manometer had water in it, and thus rho g H uses water density and delta H as above.
Please also see my attempt in the attached images for the theoretical and experimental equations.
The problem, they seem to be miles apart, am I using the correct diameters?
What am I getting wrong?
I hope you can help!
Thanks,
Max
Ive got a little stuck calculating the mass flow rate of a choked flow through a de laval nozzle.
I have been given a formula to use for theoretical max and experimental but they seem to be SO far apart, I am sure I am missing something.
Given data:
Density of water 1000 kg/m^3
Throat diameter (nozzle) 4.79mm
Exit diameter (nozzle) 5.54mm
Probe diameter 3.30mm
Coefficient of discharge of orifice plate 0.6
orifice diameter 27.03mm
pipe diameter 76.2mm
gamma ratio of specific heats 1.4
gas constant 287 J/(kg K)
Absolute zero 273 degrees c / 0 K
Delta H = 2" = 0.0508m
See useful equations in attached image.
The manometer had water in it, and thus rho g H uses water density and delta H as above.
Please also see my attempt in the attached images for the theoretical and experimental equations.
The problem, they seem to be miles apart, am I using the correct diameters?
What am I getting wrong?
I hope you can help!
Thanks,
Max