- #1
Piyush Gupta
- 2
- 0
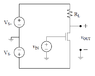
I'm trying to solve for the minimum vIN such that MOSFET is in the saturation region. Here are the given parameters
VS+ = 1.0 V
VS- = - 1.0 V
VT = 0.5 V
In order to enter saturation I know that VDS > VGS - VT
VGS = VIN - VS-
VDS = Vs+ - Vs-, which is 2 V
Which means
2V > VIN - VS- - VT
2V > VIN - (- 1.0 V) - 0.5 V
2V > VIN + 0.5 V
I get a VIN of 1.5 Volts. The correct answer is -0.5 V. I'm just starting to learn electrical engineering and it would be great if someone can point out what's missing.
VS+ = 1.0 V
VS- = - 1.0 V
VT = 0.5 V
In order to enter saturation I know that VDS > VGS - VT
VGS = VIN - VS-
VDS = Vs+ - Vs-, which is 2 V
Which means
2V > VIN - VS- - VT
2V > VIN - (- 1.0 V) - 0.5 V
2V > VIN + 0.5 V
I get a VIN of 1.5 Volts. The correct answer is -0.5 V. I'm just starting to learn electrical engineering and it would be great if someone can point out what's missing.