RmsAdd
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
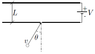
Two parallel plates located at a distance "L" from each other they maintain a potential difference "V" because of a battery (as shown in the picture). Through a small hole, made in bottom plate, electrons get into system (with mass "m" and charge "-e"), with velocity "v" and forming a θ angle with the perpendicular direction of the plate. A flourescent screen at the top plate allows to determine where the electrons impact.
If there is a small change dV at the potential difference betwen the plates. Where and how much the position where electrons impact varies? (Do not matter about relativism effects and cuatic effects). Make a scheme about the dependency of that variation with the velocity v and the angle θ.
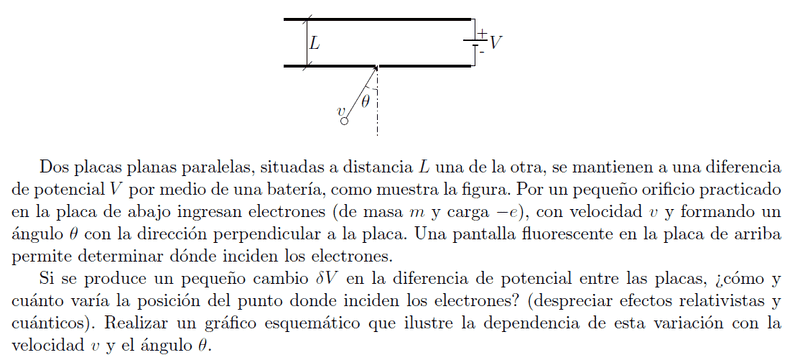
Dos placas paralelas situadas a distancia L una de la otra, se mantienen a una diferencia de potencial V por medio de una batería, como muestra la figura. Por un pequeño orificio practicado en la placa de abajo ingresan electrones (de masa m y carga -e), con una velocidad v y formando un angulo θ con la dirección perpendicular a la placa. Una pantalla fluorescente en la placa de arriba permite determinar dónde inciden los electrones.
Si se produce un pequeño cambio dV en la diferencia de potencial entre las placas, ¿Cómo y cuanto varía la posición donde inciden los electones? (despreciar efectos relativistas y cuánticos). Realizar un grafico esquematico que ilustre la dependencia de esta variación con la velocidad v y el angulo θ
Si se produce un pequeño cambio dV en la diferencia de potencial entre las placas, ¿Cómo y cuanto varía la posición donde inciden los electones? (despreciar efectos relativistas y cuánticos). Realizar un grafico esquematico que ilustre la dependencia de esta variación con la velocidad v y el angulo θ
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
Energy analisis:
The initial energy and the final energy have to be the same.
E_{f}=E{i}
E_{kf}=E_{ki}+U_{e}
\frac12 \cdot m \cdot v_{f}^{2}=\frac12 \cdot m \cdot v_{i}^{2}+F_{e} \cdot L
v_{f}=\sqrt{ v_{i}^{2}+ \frac{2 \cdot F_{e} \cdot L}{m}}\qquad \text{(1)}
Motion analisis:
\Sigma F_{x}=0
v_{x}=constant
\Sigma F_{y}=m \cdot \vec{a}
So we have a constant uniform motion in x-axis and a constant aceleration in y-axis. I can find the final velocity in y-axis using Pythagorean teorem
v_{f}^2=v_x^2 + v_{fy}^2
v_{fy}=\sqrt{v_f^2 - v_x^2}
In y-axis aceleration is constant so I can do:
V_{m}=\frac{v_{fy}+v_{iy}}{2}
V_{m}=\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta t}
\Delta t=\frac{2 \Delta y}{v_{fy}+v_{iy}} \qquad \text{(2)}
This is the time that it takes to the particle in order to reach the top plate. I can use \Delta t to get x-axis distance.
v_x=\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}
x=v_x \cdot \Delta t
Replacing with (2):
x=v_x \cdot \frac{2 \Delta y}{v_{fy}+v_{iy}}
\Delta y=L
v_x=\sin \theta \cdot v_i
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_f^2-v_x^2}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
Replacing vf with (1) and replacing vx:
Edit: I've made a mistake replacing vx^2
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}-\sin^2 \theta \cdot v_f^2}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}-\sin^2 \theta \cdot \left(v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m} \right)}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}-\sin^2 \theta \cdot v_i^2 + \sin^2 \theta \cdot \frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2(1- \sin^2 \theta) +\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}(1+\sin^2 \theta)}+ \cos \theta \cdot v_i}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}-\sin^2 \theta \cdot \left(v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m} \right)}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}-\sin^2 \theta \cdot v_i^2 + \sin^2 \theta \cdot \frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2(1- \sin^2 \theta) +\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}(1+\sin^2 \theta)}+ \cos \theta \cdot v_i}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2+\frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m}-\sin^2 \theta \cdot v_i^2}+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{v_i^2 \left( 1+ \frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m \cdot v_i^2}-\sin^2 \theta \right) }+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{v_i \sqrt{ 1+ \frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m \cdot v_i^2}-\sin^2 \theta }+v_i \cdot \cos \theta}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot v_i \cdot \sin \theta}{v_i \left( \sqrt{ 1+ \frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m \cdot v_i^2}-\sin^2 \theta }+ \cos \theta \right)}
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot \sin \theta}{\sqrt{ 1+ \frac{2 \cdot F_e \cdot L}{m \cdot v_i^2}-\sin^2 \theta }+ \cos \theta}
Finally I know that:
V=\frac{U_e}{q}=\frac{F_e \cdot L}{q}
F_e \cdot L=V \cdot q
x=\frac{2 \cdot L \cdot \sin \theta}{ \sqrt{ 1+ \frac{2 \cdot V \cdot q}{m \cdot v_i^2}-\sin^2 \theta }+ \cos \theta}
Now I've an equation which gives me the position as function of voltage. Can I do \frac{\partial x}{\partial V} in order to obtain how much the position varies in relation with small variation \partial V?
Am I doing it in a adequated way (I think that it's a really ugly equation)? Or should I consider other factors?
Attachments
Last edited: