cjavier
- 17
- 0
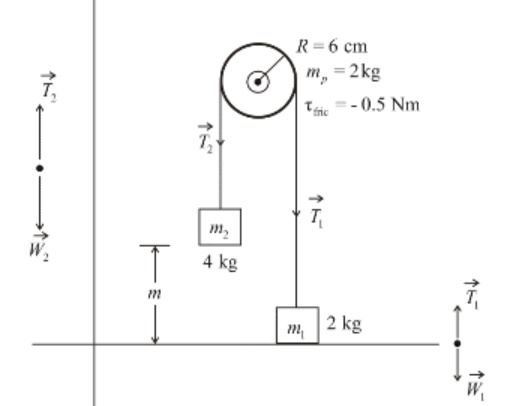
In the attached picture, one sees a pulley with a mass which is holding two different weights. In chegg, the tension due to a weight is represented as a downward direction. Then, when the tension is seen in relation to the pulley, the direction switches for both weights. WHY IS THIS?!
Thanks,
Cameron
Thanks,
Cameron