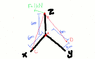
- #1
papasmurf
- 22
- 0
Homework Statement
Determine the tension in cables BC and BD, and reactions at the ball-and-
socket joint at A for the mast shown in the figure.
Answers are given by the teacher for checking purposes: TC=707 N; TD=1500 N, Ax=0 N,
AY=0 N, AZ=1500 N
Homework Equations
ƩMx=0
ƩMy=0
ƩMz=0
ƩFx=0
ƩFy=0
ƩFz=0
The Attempt at a Solution
Taking clockwise to be the positive moment direction about the x-axis. In other words, if you are standing at the positive side of the x-axis and look down towards the negative side, the moment will be spinning clockwise.
ƩMx=0= -1kN(6m) + TBDcos(tan-1(3/6))cos(45)[kN]*(6m)
...this attempt at a solution is way wrong.
The way I thought about it was, take the cos(tan-1(3/6)) to get your TBD in the yz-plane. Next, I took the cos(45) to get it going strictly in the y direction, and then multiplied by the perpendicular distance from the x-axis, 6 m. The problem I'm having is knowing what to do with the given force of 1 kN. There is no specified direction or any information stating where this force is going to. I know how to use the moment and force equations if I can get these things broken up into components correctly.