The total voltage drop in a series RLC circuit
Click For Summary
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the total voltage drop in a series RLC circuit, specifically questioning the validity of the equation relating the total voltage to the individual voltage drops across the resistor, inductor, and capacitor. Participants explore concepts related to Kirchhoff's Voltage Law, phasor representation, and the implications of using maximum versus instantaneous voltages.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
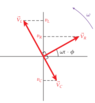
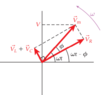
- Some participants question whether the total voltage across all components in a series RLC circuit is truly equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops, ##v_{L} + v_{C} + v_{R}##.
- One participant asserts that Kirchhoff's Voltage Law supports the idea that the loop voltage must equal the sum of individual voltage drops, suggesting confusion over scalar versus complex voltages.
- Another participant describes a scenario where the inductor's voltage was calculated to be significantly higher than the source voltage, raising questions about the validity of the first equation in light of the second equation, ##V_{m}^{2} = V_{R}^2 + (V_{L} - V_{C})^{2}##.
- There is a discussion about whether the second equation holds true for instantaneous voltages rather than maximum voltages, with references to phasor vectors and RMS values.
- Some participants highlight the importance of considering the phase of each voltage term when summing voltages in AC circuits.
- One participant suggests reviewing voltage dividers, complex impedance, and phasor representation for further understanding.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the validity of the equations related to voltage in a series RLC circuit. There is no consensus on whether the total voltage drop can be accurately represented by the sum of the individual voltage drops, and the discussion remains unresolved with multiple competing perspectives.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the equations discussed involve assumptions about voltage types (instantaneous vs. maximum) and the implications of using RMS values in AC circuit analysis. The relationship between voltage drops and gains in the context of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law is also highlighted, but remains a point of contention.
Similar threads
- · Replies 22 ·
- · Replies 32 ·
- · Replies 152 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 11 ·
- · Replies 8 ·
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 15 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 4 ·