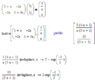- #1
- 3,483
- 1,164
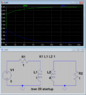
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
Kirchhoff's laws
The Attempt at a Solution
Applying KVL on primary,
di1/dt+i1=5+2di2/dt...1)
Similarly for secondary,
2di1/dt= 4di2/dt + i2...2)
After solving these equations using Laplace Transform, I got
I1= 5-e-0.2t A and
I2 = 2e-0.2t-2e-0.25t.
I have verified these answers using initial and final conditions and I believe they are correct.
However, at t=0, the energy in the system comes out to be 8J (E= 0.5L1i12+0.5L2I22-Mi1i2, since there is magnetic opposition).
How is this possible? How can the energy change instantaneously here?
For E to be zero at t=0, i2 at t=0 should be 2A. But here, i2|t=0= 0A.
What am I missing here?