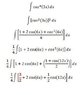SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the Power Reducing Identity in trigonometric functions, specifically the equation cos^u = (1 + cos(2u)) / 2. A participant seeks clarification on the integration process, particularly the origin of the coefficient 3/2 in the context of the integrand. The confusion arises from the combination of the constant 1 and the fraction 1/2, leading to the conclusion that 1 + 1/2 equals 3/2. This highlights the importance of correctly applying the Power Reducing Identity during integration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of trigonometric identities, specifically the Power Reducing Identity.
- Basic knowledge of integration techniques in calculus.
- Familiarity with the notation and manipulation of fractions in mathematical equations.
- Ability to interpret and analyze integrands in calculus problems.
NEXT STEPS
- Review the derivation of the Power Reducing Identity in trigonometry.
- Practice integration techniques involving trigonometric functions.
- Study the application of trigonometric identities in calculus problems.
- Explore common pitfalls in combining constants and fractions during integration.
USEFUL FOR
Students studying calculus, particularly those focusing on trigonometric functions and integration techniques, as well as educators looking for examples to clarify the Power Reducing Identity.