You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Elastic: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Elastic fibers (or yellow fibers) are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan.
Elastic tissue is classified as "connective tissue proper".Elastic fibers are formed via elastogenesis, a highly complex process involving several key proteins including fibulin-4, fibulin-5, latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 4, and microfibril associated protein 4 In this process tropoelastin, the soluble monomeric precursor to elastic fibers is produced by elastogenic cells and chaperoned to the cell surface. Following excretion from the cell, tropoelastin self associates into ~200 nm particles by coacervation, an entropically driven process involving interactions between tropoelastin's hydrophobic domains, which is mediated by glycosaminoglycans, heparan, and other molecules. These particles then fuse to give rise to 1-2 micron spherules which continue to grow as they move down from the cells surface before being deposited onto fibrillin microfibrillar scaffolds.Following deposition onto microfibrils tropoelastin is insolubilized via extensive crosslinking by members of the lysyl oxidase and lysyl oxidase like family of copper-dependent amine oxidases into amorphous elastin, a highly resilient, insoluble polymer that is metabolically stable over a human lifespan. These two families of enzymes react with the many lysine residues present in tropoelastin to form reactive aldehydes and allysine via oxidative deamination.These reactive aldehydes and allysines can react with other lysine and allysine residues to form desmosine, isodesmosine, and a number of other polyfunctional crosslinks that join surrounding molecules of tropoelastin into an extensively crosslinked elastin matrix. This process creates a diverse array of intramolecular and intermolecular crosslinks These unique crosslinks are responsible for elastin's durability and persistence. Maintenance of crosslinked elastin is carried out by a number of proteins including lysyl oxidase-like 1 protein.Mature elastic fibers consist of an amorphous elastin core surrounded by a glycosaminoglycans, heparan sulphate, and number of other proteins such as microfibrillar-associated glycoproteins, fibrillin, fibullin, and the elastin receptor.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Elastic tissue is classified as "connective tissue proper".Elastic fibers are formed via elastogenesis, a highly complex process involving several key proteins including fibulin-4, fibulin-5, latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 4, and microfibril associated protein 4 In this process tropoelastin, the soluble monomeric precursor to elastic fibers is produced by elastogenic cells and chaperoned to the cell surface. Following excretion from the cell, tropoelastin self associates into ~200 nm particles by coacervation, an entropically driven process involving interactions between tropoelastin's hydrophobic domains, which is mediated by glycosaminoglycans, heparan, and other molecules. These particles then fuse to give rise to 1-2 micron spherules which continue to grow as they move down from the cells surface before being deposited onto fibrillin microfibrillar scaffolds.Following deposition onto microfibrils tropoelastin is insolubilized via extensive crosslinking by members of the lysyl oxidase and lysyl oxidase like family of copper-dependent amine oxidases into amorphous elastin, a highly resilient, insoluble polymer that is metabolically stable over a human lifespan. These two families of enzymes react with the many lysine residues present in tropoelastin to form reactive aldehydes and allysine via oxidative deamination.These reactive aldehydes and allysines can react with other lysine and allysine residues to form desmosine, isodesmosine, and a number of other polyfunctional crosslinks that join surrounding molecules of tropoelastin into an extensively crosslinked elastin matrix. This process creates a diverse array of intramolecular and intermolecular crosslinks These unique crosslinks are responsible for elastin's durability and persistence. Maintenance of crosslinked elastin is carried out by a number of proteins including lysyl oxidase-like 1 protein.Mature elastic fibers consist of an amorphous elastin core surrounded by a glycosaminoglycans, heparan sulphate, and number of other proteins such as microfibrillar-associated glycoproteins, fibrillin, fibullin, and the elastin receptor.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
C
Gun-Projectile Elastic Collision
1. Homework Statement A projectile of 45kg has a muzzle speed of 656.6 m/s when fired horizontally from a gun held in rigid support (no recoil). What will be the muzzle speed (relative to the ground) of the same projectile when fired from a gun that is free to recoil? The mass of the gun is...- Calvin Pitts
- Thread
- Replies: 24
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Gun-projectile Elastic Collisions
So I'm reading my textbook and there's a problem asking what the muzzle speed of a projectile would be if the gun it is being fired from is free to recoil. I'm given the muzzle speed of the projectile when the gun is stationary, the mass of the projectile, and the mass of the gun. I'm also told...- Calvin Pitts
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Invariance of elastic potential energy
At non-relativistic speeds is the elastic potential energy of a compressed spring frame-invariant? That is, would all reference frames agree on how much elastic potential energy is stored in the spring? -
J
Can Elastic Potential Energy Ever Be Negative?
Homework Statement Which of the following Graphs BEST illustrates the potential energy vs. time for the system in Figure 1, where t=0 is defined as the time at which the incident box 1st contacts the box on the spring? My question is why can't the Elastic PE be negative? The answer is A...- Joseph Phan
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Collision with magnets -- Elastic or Inelastic?
In my experiment I am performing a collision with two carts with magnets attached with photogates and a labquest on an air track. I pushed the carts together and made sure that the carts did not come into contact. Based on my knowledge of collisions, I believed that the collision would have been...- ScienceStudent
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
P
Impact of a elastic string on pendulum
Hello All, I was performing an experiment in which the perod of oscllation of a pendulun at different lengths is measured using a light gate. while performing the experiment i noticed that the string was slightly elastic, differing from the perfect pendulum. I was attempting to figure... -
P
Formula for bending a rod in the elastic range
Is there a formula to calculate the radius that a rod of a given radius can be bent around while staying in the elastic range? For example, if I had a rod that was 1/4" in diameter and made of HDPE (which I think has a modulus of elasticity of 0.8 GPa), how would I calculate the minimum radius...- pistorinoj
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
P
Formula for bending a rod in the elastic range
Is there a formula to calculate the radius that a rod of a given radius can be bent around while staying in the elastic range? For example, if I had a rod that was 1/4" in diameter and made of HDPE (which I think has a modulus of elasticity of 0.8 GPa), how would I calculate the minimum radius...- pistorinoj
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

Elastic collision -- Energy & Momentum
Homework Statement Please see the attached photo. (down) Hminitial= 1.5R M = 2/3m Perfectly elastic collision What is the velocity of object m immidiatly after the collision? (by m,g,R) Homework Equations Conservation of energy Conservation of momentum The Attempt at a Solution I assumed...- Deadawake
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Velocity from an elastic collision
Homework Statement A body X moving with a velocity v makes an elastic collision with a stationary body Y of equal mass on a smooth horizontal surface. Which statement gives the velocities of the two bodies after the collision? (multiple choice question)The Attempt at a Solution The answer...- Millie Baker
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Energy in an elastic collision
Homework Statement This is not really a homework problem, just me trying to get a ballpark number for a random problem. Suppose I have a neutron flying at some energy and it hits an oxygen atom. If the oxygen atom, after the collision, now has 20 keV of energy, but before, had ~ 0, is there a...- sportcardinal90
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Spring elastic potential, removing mass
Homework Statement 5 identical masses M are suspended by a spring stretched a distance of L. If 3 of these masses are removed, what is the potential energy stored in the spring? 2. Relevant diagram So L is the distance stretched with 5 masses. Let L2 be the distance stretched with 2 masses...- HaoPhysics
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
MATLAB Solving an Elastic Pendulum Equation with Matlab/Excel
Hi guys, I need to transform Newtonian solution of motion equation for spring (elastic) pendulum into Matlab or Microsoft Excel. I want to use Euler´s Method (or Runge Kutta Method) of numerical solution for that problem. I know all the equations but I have a problem with making some code from...- nneutrino
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: MATLAB, Maple, Mathematica, LaTeX
-
J
Finding the elastic modulus of a metal in a mixed phase
Homework Statement If a metal is adhered to a surface of another metal, let's say copper is plated onto aluminum, how can the elastic modulus of copper can be extracted given only the data of the thickness of the copper and aluminum, the young's modulus of the combined metal and the modulus of...- joemmonster
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
Two-Dimensional Elastic Collision of Equal Masses
Homework Statement Show that if an elastic collision between a mass and a stationary target of equal mass is not head-on that the projectile and target final velocities are perpendicular. (Hint: Square the conservation of momentum equation, using ##p^2=p\cdot p##, and compare the resulting...- flamespirit919
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How to solve a simple elastic collision problem?
Homework Statement "A particle with mass ##m_1=1kg## traveling at ##v_{1_{0}}\frac{m}{s}## collides with a stationary particle with mass ##m_2=2kg##. How small is the speed of ##m_1## after the collision compared to before?" Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution...- Eclair_de_XII
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I
Elastic Collision in two dimensions question
Homework Statement [/B]A 2.0 kg ball moving with a speed of 3.0 m/s hits, elastically, an identical stationary ball as shown (The first ball is traveling to the right). If the first ball moves away with angle 30° to the original path, determine the speed of the first ball after the collision...- iwatchcredits
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Why does the equation for elastic collisions work like this?
Hi guys. Feels dumb coming back to this but I seem to have confused myself I was helping a friend with the problem: You shoot protons going v=4.2e7 m/s through a particle accelerator. They collide with gas particles of an unknown mass (pretend no velocity) and all bounce back elastically at...- minnyveller
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Mechanics
-
S
Dynamics Questions // Elastic Collision with different Vo
Homework Statement [/B] A 2.3 kg object traveling at 6.1 m/s collides head-on with a 3.5 kg object traveling in the opposite direction at 4.8 m/s. If the collisions is perfectly elastic, what is the final speed of the 2.3 kg object? Homework Equations Conservation of Energy: 1/2 m*vi^2 = 1/2...- sunnnystrong
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
Elastic attached to a Car travelling down an inclined plane....
Hey! I'm conducting an experiment wherein a car of various weights travels down an inclined plane of varying angles, attached to the back of the car and the top of the ramp is an elastic cord. Once the car reaches the end the elastic pulls backward, and thus pulling the car back. We are...- Samil
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Analysis of collisions from data
Good afternoon! I would like to preface by saying, yes, this is for a project. I am only posting here to see if my method of solving is correct before I finish the project incorrectly. Homework Statement I chose two balls, mass A: .553 kg and mass B: .410 kg I recorded their collision and...- xjcov
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
S
I Level of unseen elastic scatterings
How often are visible matter particles seen to undergo elastic scattering with particles that remain otherwise unseen? Known particles that may cause such scattering include neutrinos and antineutrinos (three flavours each) which are also seen in inelastic destruction and formation processes...- snorkack
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Elastic
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
J
Elastic collision between pool balls
Homework Statement A super cue ball is made of the same material with the target ball (radius r) but slightly larger: rc = (3)^(1/3)*r The cue ball collides with the target ball on a frictionless table, as shown below, with initial speed of v0. The collision is not head-on, as shown below. a)...- John004
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Y
Relativistic elastic collision
Homework Statement Homework Equations et Em and pm be the energy and momentum of the mass m after the collision. Let p and p' be the momentum of mass M before and after the collision. From conservation of 4 momentum: \begin{bmatrix}E+m \\ p\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}E_m+E' \\...- yup790
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Conservative force for an elastic force?
Hi , I wanted to know how elastic force could be a conservative force ? -
R
Hooke's law and elastic deformation
The Attempt at a Solution [/B] I know that spring A shows elastic deformation since it returned to its original shape once the stress removed and spring c shows plastic deformation and has been permanently extended so it won't return to its original shape. BUT, I'm struggling to complete the...- ravsterphysics
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Deformation Elastic Hooke's law Law
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Can someone explain elastic band physics
in my physics class we have to create a device that will make an egg not break after being dropped from a second story window. my idea was to take a strength training resistance band and use it like a bungee jumping cord and have the egg drop to the bottom without breaking. what are the formulas... -

2 masses colliding (elastic)
Homework Statement Mass 1 has a mass of 5kg and is traveling with an initial velocity of 20 m/s at a 45 degree angle. (Starting in Quadrant II and heading toward the origin.) Mass 2 has a mass of 6kg and is traveling with an initial velocity of 15 m/s at a 45 degree angle. (Starting in...- blixel
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Elastic
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
N
Find the height the block rises to after an elastic collision
Homework Statement Two blocks are free to slide along a frictionless wooden track ABC as shown below. The block of mass m1 = 5.09 kg is released from A. Protruding from its front end is the north pole of a strong magnet, repelling the north pole of an identical magnet embedded in the back end...- Neon32
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Difference between elastic and coherent scattering
Hi everyone! What is the difference between coherent and elastic scattering. Maybe the elastic scattering implies that there is not loss of energy, whereas the coherent scattering implies that the wavelength of a ray (or rays) is the same before and after the scattering? Thank you in advance. -
P
Electron to Stationary Proton Collision
Homework Statement A 2 GeV electron is incident on proton (m_p * C^2 = 0.938 GeV) target at rest. Calculate the invariant mass of the electron-proton pair in the Center of Mass(CM) frame. Neglect the mass of electron which is much less than the proton mass.Homework Equations M = [P1 + P2)][/2]...- PatrickStar
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
M
Elastic deformation is time-indipendent
"Elastic deformation is time-indipendent." What does this sentence refer to? It makes no sense to me. Source: http://www.nobelyayin.com/sunumlar/malzeme/callister/ (page 11) Thank you.- mech-eng
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Deformation Elastic
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-

Oscillating Formation of Spherical Mass in elastic universe
Situation, a empty universe where there are only concentric spherical shells of mass dm spaced apart by distance dx and contracts under gravity to form a sphere. Assume that there is a point mass in the middle of all the shells. I don't think it would work without it. case1 is an inelastic...- FallenApple
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Mechanics
-
A
Find V2 of an elastic equation
Homework Statement A 0.038-kg pet lab mouse sits on a 0.35-kg air-track cart, as shown in (Figure 1) . The cart is at rest, as is a second cart with a mass of 0.25 kg. The lab mouse now jumps to the second cart. After the jump, the 0.35-kg cart has a speed of v1=0.86m/s. What is the speed v2...- Angela_vaal
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Elastic
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Elastic and gravitational potential energy
X has a mass of 55 kg and hangs from a rope. As a result of this the rope stretches by 0.6 m. Calculate the energy stored in the rope as a result of stretching. Solution: F = kx and E = 0.5x^2. Using this fetches the answer as 161.5 However, the change in potential energy (calculated using mgh )...- Pratik89
- Thread
- Replies: 49
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
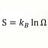
Momentum Transfer: Elastic Collision vs Inelastic Collision
In elastic collision momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. Where as in inelastic collision K.E. and P are not conserved since K.E. lost during deformation in target object is consistent with momentum conservation. The question here is in context of working out with a 70kg heavy bag (m2 )... -
P
What is the Fraction of Energy Lost by an Electron in Elastic Scattering?
Homework Statement An electron collides with a particle with mass M at rest and scatters elastically through an angle θ (assume electron mass negligible). Show that the fraction of energy lost by the e- is: (Ee - Ee')/Ee = 1/[1+ Mc2/Ee(1-cosθ)] Homework Equations Conservation of Energy: Ee +...- Poirot
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
O
Elastic Pendulum with Newton's equations of motion
Homework Statement A pendulum with a mass m hanging on a elastic bug rigid massless rod which may swing in the xy-plane. The pivot point is the origin of the coordinate system. The force acting on the pendulum is the sum of force of an elastic central force directed towards the origin, and...- ojb89
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Two dimensional Elastic Collision
Homework Statement [/B] The problem statement is: A helium atom traveling at a speed of 240 m/s hits an oxygen atom at rest. If the helium atom rebounds elastically, from the oxygen atom at an angle of 90° with respect to the original direction of motion, what are the final velocities of both...- CalebB-M
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
Elastic collision with pendulum
Homework Statement A steel ball of mass 0.890 kg is fastened to a cord that is 50.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal, as shown in the figure. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 2.50 kg steel block initially at rest on a...- Jrlinton
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
2D elastic collision in CM Frame, velocities antiparallel?
Homework Statement Why are the Center of Momentum velocities of masses after a 2D elastic collision anti-parallel? (as in the following diagram) Homework Equations CM_Velocity = (∑m_i*v_i)/(∑m_i) The Attempt at a Solution This is not actually a problem I have to do. I am just looking for a...- hsbhsb
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
Understanding elastic tensor matrix intuitively
Hi, I know the generalized hookes law between stress and strain is given by the elastic tensor. This matrix has 81 constants which are reduced to 9 in the isotropic case. Can someone please help me to understand intuitively how this reduction in the elastic tensor takes place and why some of the...- chiraganand
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
Z
Two bodies on elastic spring system
Homework Statement A body of mass M is connected to a vertical spring.Another body of mass m is placed on it.Calculate the amplitude of the oscillation of that system,with the condition that the body m always stays on top of body M(no jumps).No friction. Homework Equations mg=kx mgh=0.5kx2...- zvonecar13
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Particle motion when wrapped around drum; elastic string
Homework Statement A uniform cylindrical drum of mass M and radius a is free to rotate about its axis, which i is horizontal. An elastic cable of negligible mass and length l is wrapped around the drum and carries on its free end a mass m. The cable has elastic potential energy \tfrac12...- Dazed&Confused
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
J
I Limiting behavior of quantum elastic collision
From the hyperphysics site http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/elacol2.html#c1 on classical elastic collisions I see that if an incoming particle of mass ##m_1## with velocity ##v_1## collides into a stationary target particle of mass ##m_2## then the velocity of the target particle after...- jcap
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
P
Energy transfer in elastic collision.
How do I derive the energy transfer equation in an elastic collision of two bodies of masses m and M respectively,using the energy and momentum conservation relations in the laboratory frame? $$\frac{1}{2} m_1 v_0^2 = \frac 1 2 m_1 v^2 + \frac 1 2 m_2 V^2$$ $$m_1 v \cos(\phi)=m_1 v_0 -m_2 V... -
E
How Is the Total Maximal Elastic Energy Calculated in This System?
Homework Statement Given the scheme https://www.dropbox.com/s/nm943gleo2nc8ft/Screenshot%202016-08-28%2013.47.33.png?dl=0 Springs' constant k=40 N\m mass of bulk m=6kg The wooden bulk is released at rest when all the springs are not stretched Question: What is the elastic total maximal Energy...- Edothegray
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Elastic Section Modulus vs Moment of Inertia
Hi everyone! Please help, I have spent a considerable time to understand the two concepts and still this is nagging at me... I am relating to Structural Engineering, just to let you know guys. My question is .. Moment of inertia is about distribution of mass, the further away from the axis the...- Peter10
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: General Engineering
-
I
Elastic Collision: Understanding the Role of Positive and Negative Signs
Hi guys. There is a question that confusing me for a long time. If an elastic collision occur, do I need to consider the positive and negative sign?? According to my teacher, an object moves in the opposite direction we need to consider the sign. Is it works in this situation? -
A
Solve for 2D Elastic Collision: Find θ & φ Angles
Homework Statement A 2D elastic collision: Two pucks (masses m1 = 0.5 kg and m2 = 0.3 kg) collide on a frictionless air-hockey table. Puck 1 has an initial velocity of 4 m/s in the positive x direction and a final velocity of 2 m/s in an unknown direction, θ. Puck 2 is initially at rest. Find...- amanda.ka
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help