- #1
grotiare
- 5
- 4
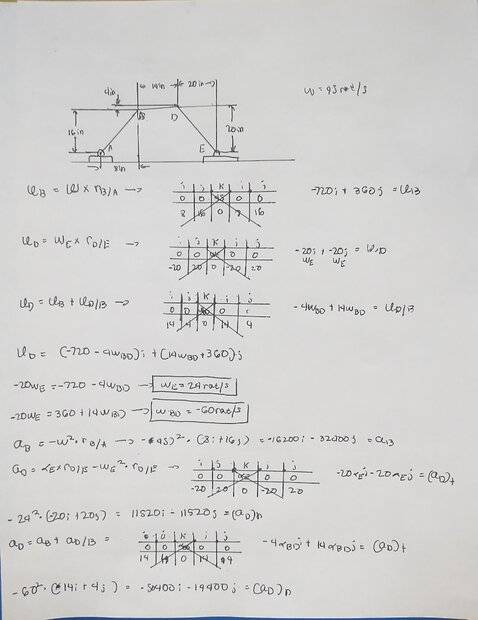
- Homework Statement
- angular acceleration of link BD and ED
- Relevant Equations
- Kinematics of rigid body formulas
Dynamics Rigid body Kinematics problem, looking for angular acceleration of link BD and ED. AB has constant angular velocity of 45 rad/s CCW. Could y'all verify any mistakes in my solution? Thanks!