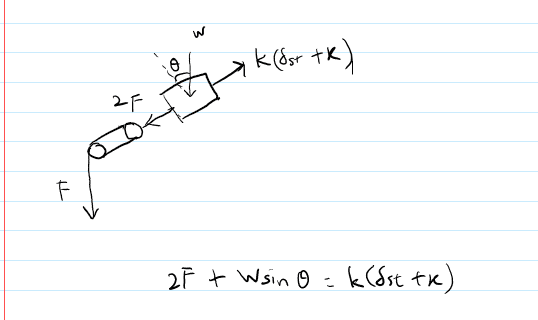Homework Help Overview
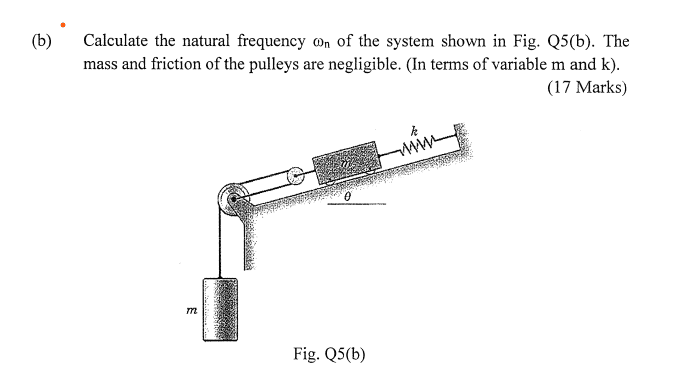
The discussion revolves around expressing the natural frequency, ωₙ, in terms of mass (m) and stiffness (k) within the context of a mechanical system involving pulleys and masses. Participants explore various approaches to derive this expression, questioning the underlying principles and assumptions involved.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning, Problem interpretation, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- The original poster attempts to simplify the relationship between force and displacement using Hooke's law but struggles to isolate ωₙ in terms of m and k. Other participants inquire about the meaning of ##\delta_{st}## and its relevance to the problem, suggesting the use of free body diagrams and Newton's laws. There is also mention of using energy methods to derive the natural frequency.
Discussion Status
Participants are actively engaging with the problem, offering different methods to approach the derivation of ωₙ. Some have suggested using energy conservation principles, while others are focused on applying Newton's laws. There is no explicit consensus on the best approach, but multiple lines of reasoning are being explored.
Contextual Notes
There are references to specific terms like ##\delta_{st}##, which may require clarification. The discussion also highlights the need for a free body diagram and the constraints imposed by the pulley system, indicating that certain assumptions about the system's configuration are under consideration.